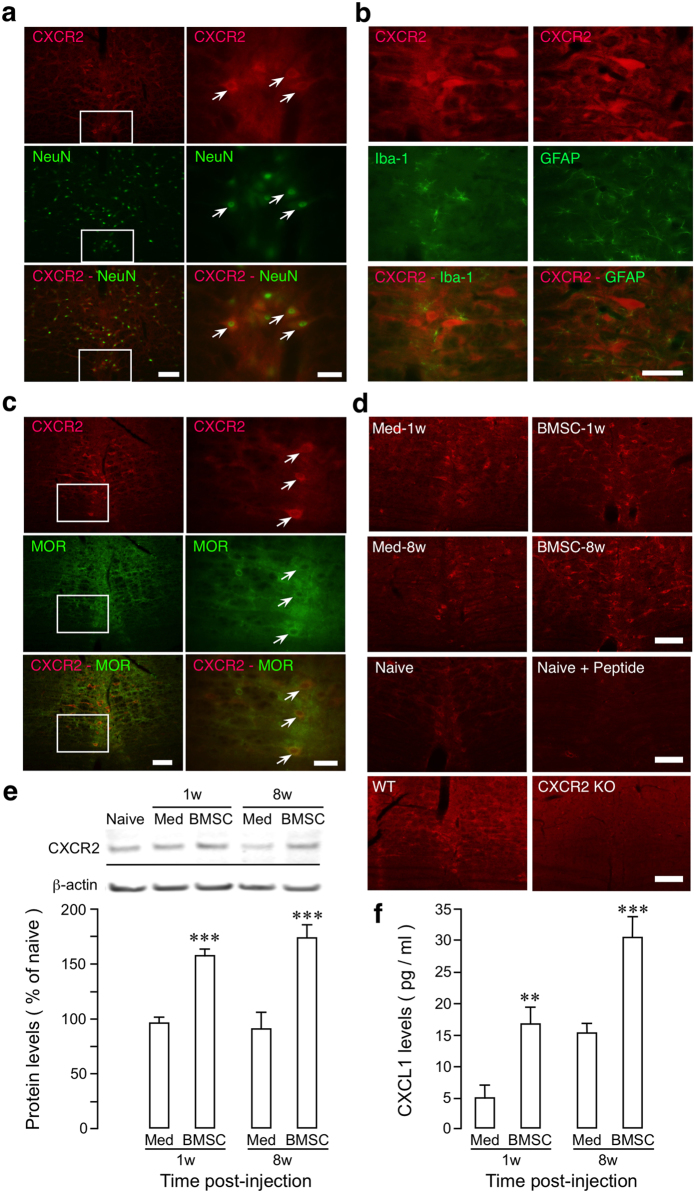
Figure 5.
Co-localization of CXCR2 with MOR and BMSC-induced upregulation of CXCR2 in the RVM and CXCL1 in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). (a) Double immunostaining showing localization of CXCR2-like immunoreactivity (red) in RVM neurons (NeuN, green). Small rectangles on the left are enlarged to the right, illustrating examples of double-labeled neurons (arrows). (b) Lack of colocalization of CXCR2-immunoreactivity with glial markers Iba-1 (microglia) and GFAP (astroglia). (c) Colocalization of CXCR2-immunoreactivity with MOR in RVM. For (a,b,c) Scale = 0.05 mm. (d) Top four images show increased CXCR2-immunoreacitivty in RVM at 1w and 8 w after primary BMSC infusion in TL rats, compared to medium-infused rats. Bottom images show CXCR2 immunostaining in naïve rats and wide type (WT) mice and loss of staining after incubation with blocking peptide for anti-CXCR2 antibody and in CXCR2 knockout mice. Scale = 0.1 mm. (e) TL rats received primary BMSCs or culture medium at 7d post injury and RVM tissues were collected. An example of western blot is shown on top and the relative protein levels are shown in the bottom. β-actin was a loading control. CXCR2 proteins were upregulated in RVM at 1w and 8w after injection of BMSC. ***p < 0.001, vs. Med, n = 4/group. Cropped gel images are shown. See Supplementary Figure 9 for full-length blots. (e) TL rats received primary BMSC or culture medium at 7d post injury and CSF was collected. Compared to medium-treated rats, CXCL1 proteins were increased in CSF at 1w and 8w after injection of BMSC. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, vs. Med, n = 4/group. Statistics: One-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc comparisons with Bonferroni corrections.