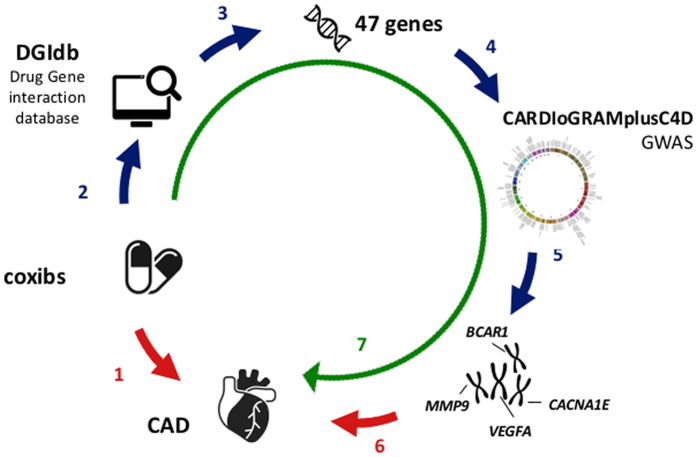
Figure 1.
Experimental Strategy: 1. Cox 2 inhibitors (coxibs) are known to increase coronary risk. 2. All genes known to be targets of coxibs were extracted from the Drug-Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb). 3. DGIdb revealed 47 genes that interact with coxibs. 4. All common variants at the chromosomal regions representing the 47 genes were subjected to a large-scale association study. 5. Four genes displayed significance for association with CAD risk. 6. These genes are candidate risk genes for CAD. 7. It may be hypothesized that the genes affected by coxibs and here shown to associate with CAD risk participate in the adverse effects of the drugs. Some drawings were obtained and used under license from Shutterstock.com (https://www.iconfinder.com/licenses/basic). Images can be found under: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/chromosomes-vector-icon-style-flat-symbol-323629910?src=library, https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/organ-heart-icon-310580756, https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/dna-icon-397249525, https://www.shutterstock.com/image-vector/pills-medication-vector-icons-set-131402543?src=library, https://www.iconfinder.com/icons/240302/find_computer_find_desktop_look_for_desktop_search_search_desktop_icon#size=128.