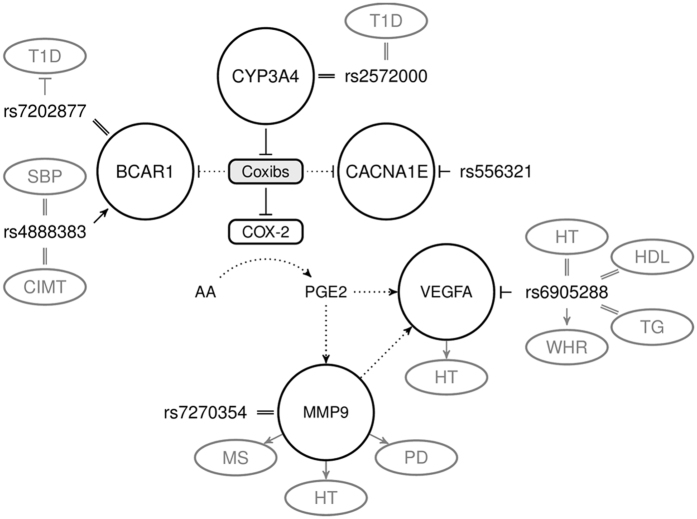
Figure 3.
Pharmacodynamic effects of coxib treatment related to the genetic association signals. All SNPs and their functional implication are shown based on the CAD risk allele. The rs numbers indicate the lead SNPs and their hypothesized function. rs6905288 is strongly associated with waist-to-hip-ratio and rs7202877 with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Suggestive associations were reported for rs4888383 with carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) and systolic blood pressure (SBP), for rs6905288 with hypertension (HTN), HDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides (TG), and for rs556321 with obesity (OB) and blood metabolites (BM). CAD risk allele rs556321 is associated with decreased expression of CACNA1E, rs4888383 is associated with decreased expression of BCAR1 and rs6905288 is associated with decreased expression of VEGFA. Functional links: ↑ (induction), ┬ (inhibition), ║(unknown effect). Dotted lines indicate potential intermediate functional link. AA: arachidonic acid, COX-2: Cyclooxigenase-2, PGE2: prostaglandin E2, VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor A, MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase-9, BCAR1: breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance protein 1, CACNA1E: calcium channel, voltage-dependent, R type, alpha 1E subunit. PD: Plaque disruption, MS = Metabolic Syndrome, T1D: type 1 diabetes, CIMT: carotid intima media thickness, SBP: systolic blood pressure, HTN: hypertension, HDL: HDL-cholesterol, TG: triglycerides, OB: obesity, BM: blood metabolites. For references see supplement.