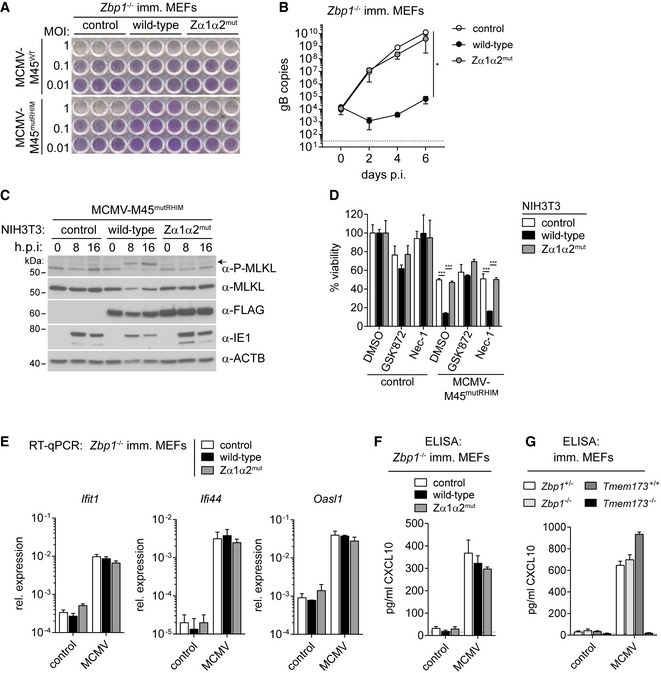
Figure 2. ZBP1 restricts MCMV replication by inducing necroptosis but not IFN expression.
-
AImmortalised Zbp1 −/− MEFs reconstituted with wild‐type or mutant ZBP1 were infected as indicated. After 5 days, cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet.
-
BImmortalised Zbp1 −/− MEFs reconstituted with wild‐type or mutant ZBP1 were infected with MCMV‐M45mutRHIM at an MOI of 0.01. DNA samples were collected at 0, 2, 4 or 6 days after infection and analysed by qPCR. gB copy numbers were derived from a titration using defined amounts of gB plasmid. The dotted line represents the lower limit of detection.
-
CNIH3T3 cells reconstituted with wild‐type or mutant ZBP1 were infected as indicated using an MOI of 3. After 0, 8 or 16 h, cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis under reducing conditions using the indicated antibodies. The arrow indicates phosphorylated MLKL.
-
DNIH3T3 cells reconstituted with wild‐type or mutant ZBP1 were infected with MCMV‐M45mutRHIM at an MOI of 10. Cells were simultaneously treated with 3 μM GSK'872 (RIPK3 inhibitor) or 30 μM Nec‐1 (RIPK1 inhibitor) or 0.1% DMSO as a control. Cell viability was analysed 24 h after infection as in Fig 1B.
-
EImmortalised Zbp1 −/− MEFs reconstituted with wild‐type or mutant ZBP1 were infected with MCMV‐M45mutRHIM at an MOI of 3. RNA samples were collected 8 h after infection and analysed by RT–qPCR.
-
F, GCXCL10 was analysed by ELISA in supernatants from MEFs of the indicated genotypes infected with MCMV‐M45mutRHIM (MOI = 3; 8 h post‐infection). The dotted line represents the lower limit of detection.
