Figure 2.
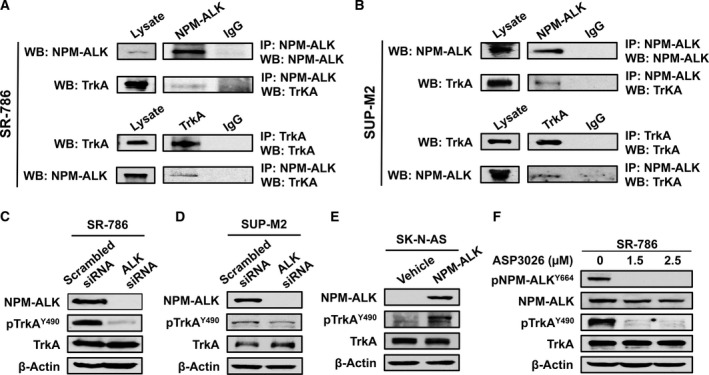
The association and interactions between TrkA and NPM‐ALK. (A) IP using ALK antibody followed by WB using TrkA antibody shows that TrkA and NPM‐ALK are physically associated in SR‐786 (A) and SUP‐M2 cells (B). Similar results were obtained when TrkA and ALK antibodies were used for IP and WB, respectively. Input levels are shown where lysates were probed only with ALK or TrkA antibody. In addition, controls are shown where IgG was used for IP. Similar results were also obtained in Karpas 299 cells (Fig. S1A). (C) and (D) Specific downregulation of NPM‐ALK using ALK siRNA was associated with remarkable decrease in the phosphorylation levels of TrkA in SR‐786 and SUP‐M2 cells, which suggests functional interactions between the two kinases. (E) In agreement with this idea, forced expression of NPM‐ALK in SK‐N‐AS cells was associated with a pronounced increase in TrkA phosphorylation levels. (F) In addition, selective inhibition of ALK kinase activity by treating the SR‐786 cells with ASP3026 for 48 h caused remarkable downregulation of pNPM‐ALK. The decrease in pNPM‐ALK was also associated with downregulation of pTrkA. ASP3026 did not induce changes in the basal levels of NPM‐ALK and TrkA. In WB experiments, β‐actin supports equal protein loading. MW: TrkA and pTrkA, 140 kDa; NPM‐ALK and pNPM‐ALK, 80 kDa.
