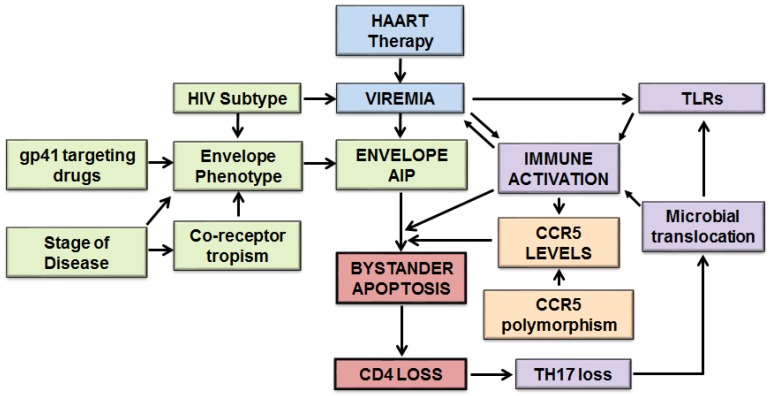
Figure 1.
Model of host and viral factors in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-mediated bystander apoptosis. HIV mediated bystander apoptosis and CD4 decline can be attributed to both host and viral factors. Fundamental to this process is active virus replication (viremia) as suppressing virus replication via highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) suppresses the major immunopathological variables of the disease including CD4 apoptosis and immune activation. The phenotype of the Envelope (Env) glycoprotein is another major determinant of HIV pathogenesis as the Env apoptosis inducing potential (AIP) correlates with CD4 loss. Other genotypic and phenotypic variations in Env like coreceptor usage, virus subtype, fusogenic activity of Env, etc. have been associated with disease. The binding of Env to CCR5 is also fundamental to HIV induced bystander apoptosis and variations in CCR5 levels can influence this phenomenon. Immune activation is a key immunopathological feature of HIV infections that correlates with CD4 decline and can be affected via multiple pathways as shown by arrows. TLR: toll-like receptor).