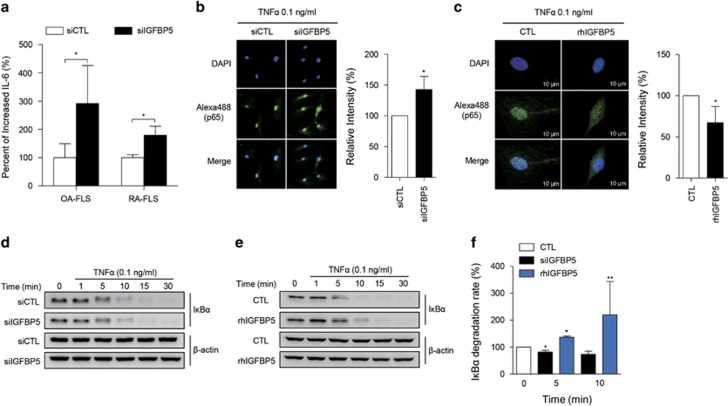
Figure 4.
IGFBP5 modulation of IL-6 production and NF-κB activation in RA-FLSs. (a) Increase in TNFα-induced IL-6 production by IGFBP5 knockdown. RA-FLSs (2 × 104 cells, n=4) and OA-FLSs (n=4) were transfected with control siRNA (siCTL) or IGFBP5 siRNA (siIGFBP5). After 24 h, the cells were stimulated with 0.1 ng ml−1 of TNFα for 12 h. IL-6 levels in culture supernatants were then determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (b, c) IGFBP5 modulation of NF-κB p65 translocation to the nucleus in RA-FLSs. RA-FLSs (2 × 103 cells) were transfected with siIGFBP5 for 24 h (b) or pre-treated with recombinant human IGFBP5 (rhIGFBP5, 50 ng ml−1) for 24 h (c), and then stimulated with 0.1 ng ml−1 of TNFα for 1 h. NF-κB p65 translocation was assessed by immunocytochemistry using an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-p65 antibody. Bar graphs in the right panel show mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. *P<0.05. (d–f) IGFBP5 regulation of IκBα degradation in RA-FLSs. RA-FLSs (1 × 105 cells) were transfected with siIGFBP5 for 24 h (d) or pre-treated with rhIGFBP5 (50 ng ml−1) for 24 h (e), and then stimulated with 0.1 ng ml−1 of TNFα for the indicated times. IκBα expression in the cells was determined by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as an internal control. Bar graph in f shows the mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.