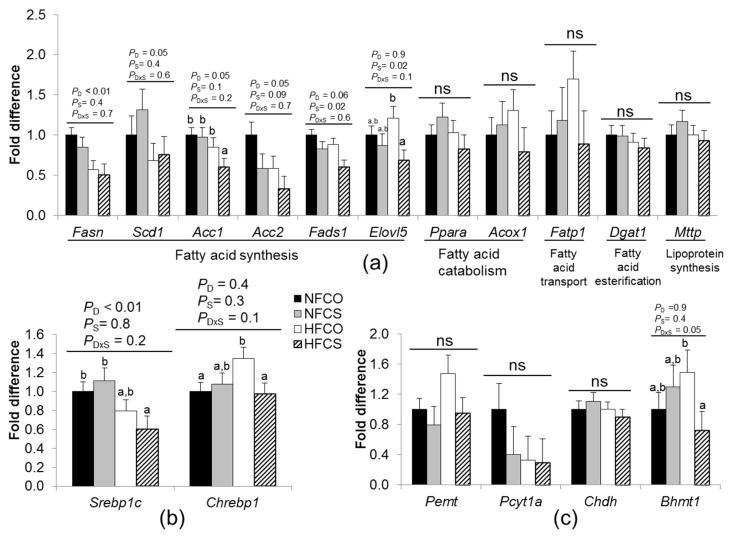
Figure 4.
Fetal liver mRNA abundance at E17.5. Experimental diets were fed to dams from 6 weeks before timed-mating to gestational day 17.5. (a) Genes involved in lipid metabolism; (b) transcription factors; (c) genes involved in choline metabolism. mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR. Data were analyzed using the general linear model. Data were analyzed using the general linear model. Posteriori analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by posthoc Fisher's least significant difference (LSD) analysis between groups was conducted with pd×s ≤ 0.2. NFCO (solid bars): n = 9; NFCS (shaded bars): n = 6; HFCO (open bars): n = 7; HFCS (hatched bars): n = 6. n is the number of dams. Data from two fetuses in each dam were pooled and included in the analysis. Values are mean ± standard error of mean (SEM); different letters indicate p < 0.05 in the posthoc analysis; ns: pd, pS, and pd×s, not significant. Acc: acetyl-CoA carboxylase; Acox1: peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1; Bhmt: betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase; Chdh: choline dehydrogenase; Chrebp1: Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein; Dgat1: diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1; Elovl5: fatty acid elongase 5; Fasn: fatty acid synthase; Fatp1: fatty acid transport protein 1; Mttp: microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; Pcyt1a: choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A; Pemt: phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase; Ppara: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; Scd1: stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; Srebp1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; CO: control; CS: choline supplemented; D: diet; HF: high-fat diet; NF: normal-fat diet; S: supplementation.