Fig. (2).
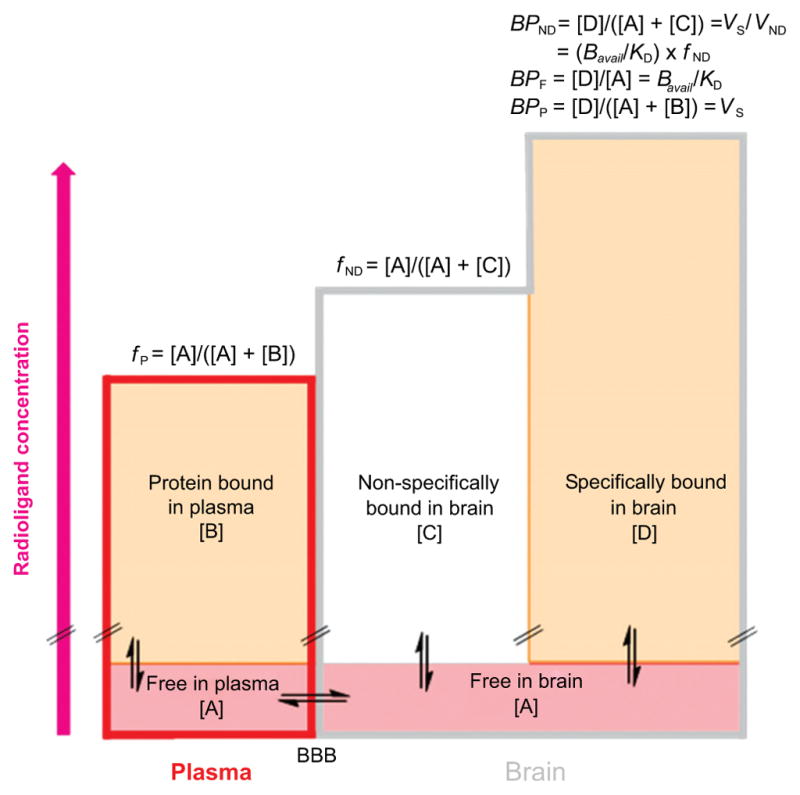
Graphical representation of the distribution of a PET radioligand between plasma and 2 tissues in brain at equilibrium. The height of each rectangle represents radioligand concentration. The free concentration of radioligand in plasma and brain is assumed to be the same and equal to [A], because of assumed free unhindered bidirectional passive diffusion across the BBB. The plasma free fraction of radioligand, fP, is the ratio of free radioligand concentration [A] to total radioligand concentration in plasma i.e.; free [A] plus protein bound [B]. Similarly, the brain free fraction of a radioligand, fND, is the ratio of free radioligand concentration [A] to the sum of free [A] and nonspecifically bound [C] radioligand concentrations in brain. [D] Represents the specifically bound concentration of radioligand in brain. Some mathematical relationships of binding potentials to other parameters are shown above the right column.
