Figure 2.
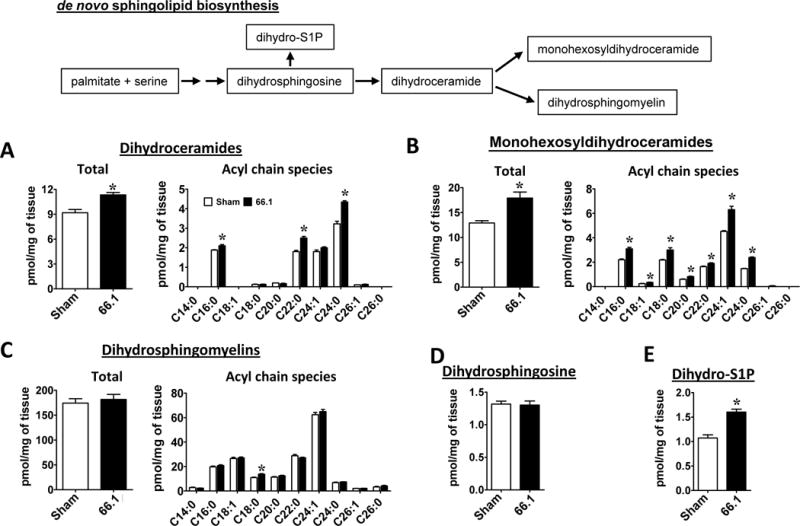
Enhanced de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis and increased dihydro-S1P levels in spinal cords of 66.1 bone tumor bearing mice. Lumbar spinal cord ipsilateral to the site of arthrotomy was harvested 14 days post-surgery from sham and 66.1 tumor-bearing mice and dihydrosphingolipid levels determined by LC-ESI-MS/MS. (A) Total dihydroceramide and its acyl chain species. (B) Total monohexosyldihydroceramide and its acyl chain species. (C) Total dihydrosphingomyelin and its acyl chain species. (D) Dihydrophingosine and (E) dihydro-S1P. Data are representative of two individual experiments and expressed as mean ± SEM for n=5 mice/group and analyzed by Welch’s corrected, unpaired, one-tailed Student’s t-test. False discovery rate was controlled by Benjamini-Hochberg procedure (q<0.05; q*=0.031). *P<0.03 vs. sham.
