Fig. 3.
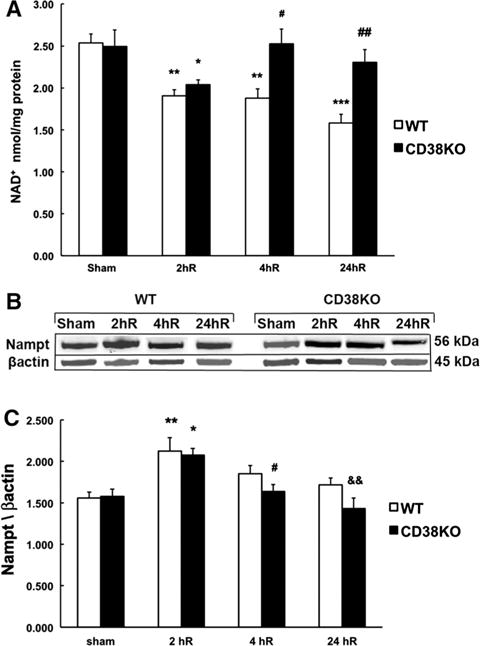
CD38 contributes to delayed post-ischemic NAD+ catabolism. a At 2 h of recovery (2hR) both WT and CD38KO animals show a reduction in hippocampal NAD+ levels, however, following 4 h of reperfusion in CD38KO mice the NAD+ recovered to pre-ischemic levels and was further reduced in WT animals. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when the post-ischemic groups are compared to corresponding sham group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 when compared to WT ischemia group, ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keul test, n = 6. b, c There was no significant difference in expression levels of the rate-limiting NAD+ synthesis enzyme Nampt between sham or post-ischemic CD38KO animals and WT animals. However, the Nampt expression was significantly increased in both WT and CD38KO mice at 2 h of recovery. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, when compared to corresponding sham groups, #p < 0.05 when compared to 2hR CD38KO, &&p < 0.01 when compared to 2hR CD38KO, ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keul test, n = 6
