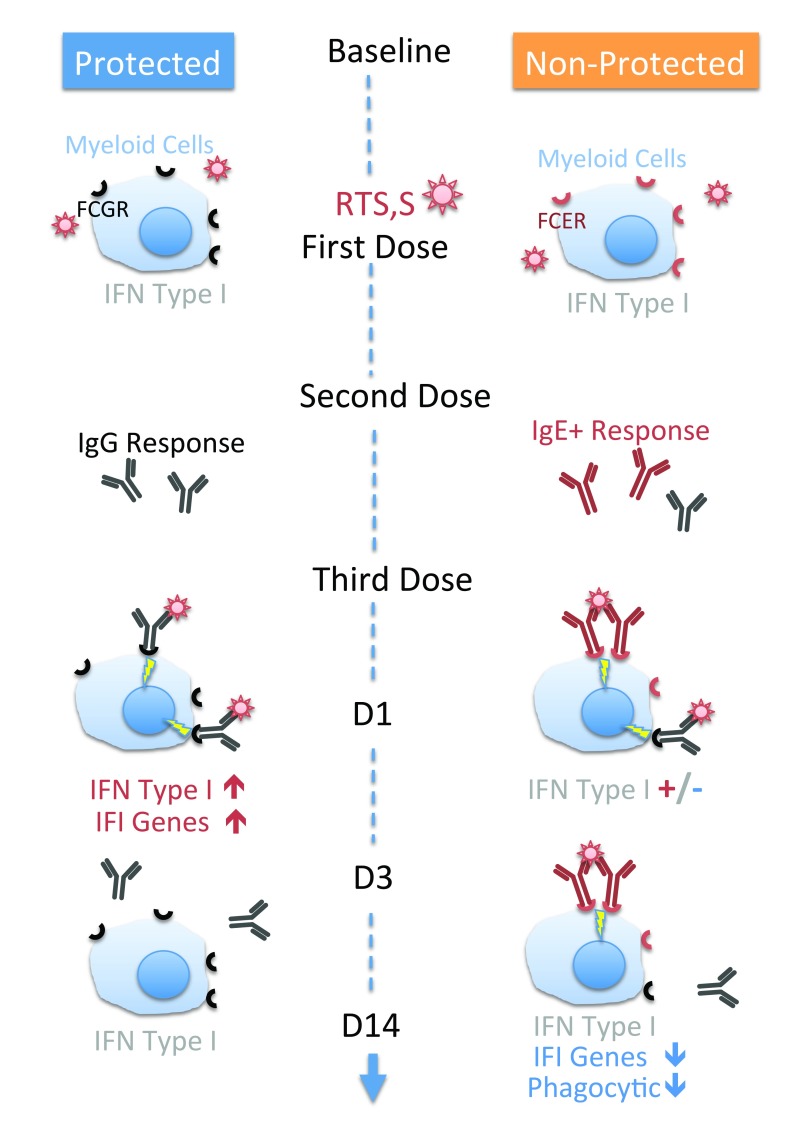
Figure 3. Proposed immunological mechanism determining protection – or lack thereof – in adult human individuals to whom was inoculated the RTS,S vaccine.
Our model infers that the interferon signatures observed on days 1, 3 and 14 post-vaccination correlating with outcome of the processes that deploy post the co-delivery of Anopheles saliva and P. falciparum sporozoites, are the result of engagement of Fc receptors by immune complexes. According to our model no interferon signatures should be observed following administration of the first vaccine dose of the CSP- containing RTS,S vaccine, in absence of pre-existing immune effectors/regulators reactive to P. falciparum Circum Sporozoite Protein/CSP. The injection of the first two doses of vaccines should elicit a humoral response, which in non-protected individuals is dominated by CSP- binding IgE rather than IgG. CSP- Ig- immune complexes should form when the third vaccine dose is administered. The transient interferon response elicited in individuals who develop a protective response and that we observed at Day 1 could be mediated by engagement of the FcγR by IgG-CSP immune complexes as has been described earlier in the context of influenza vaccination) 25. Our model predicts that IgE-CSP complexes form in non-protected individuals and cross-link the high affinity IgE receptor at the surface of cells of the myeloid lineage. FCER1 engagement would in turn mediate reduction in levels of IFN-inducible transcripts that is observed on days 3 and 14. This reduction of constitutive levels of IFN-inducible transcripts in the non-protected group would be countered at least partially on Day 1 by residual IgG-IC response in subjects displaying mixed IgE/IgG humoral responses. If this is indeed the case the levels of M1.2 reduction on Day 1 in individuals displaying CSP-binding IgE should be inversely correlated with levels of CSP-specific IgG. Given the transient nature of the interferon signature that was observed and that we tentatively attribute to IgG ICs, this partial reversal of IgE mediated suppression would not be observed at later time point, which would account for the sustained decrease in abundance of interferon-inducible transcripts that was observed at days 3 and 14. Engagement and crosslinking of FCER1 may also result in altered phagocytic and parasite killing abilities 33 thus potentially contributing to diminished resistance to infection in cases where the humoral response to RTS,S vaccination is dominated by IgE.