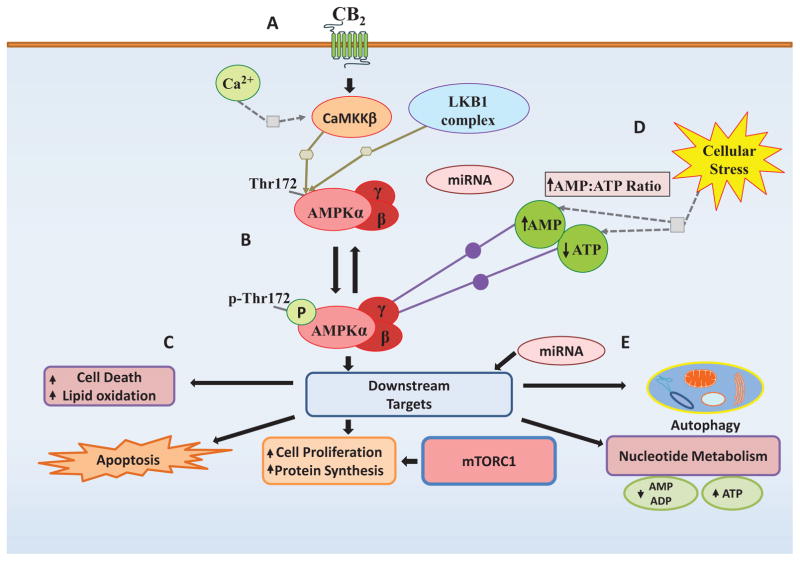
Fig. (1). Regulation of the AMPK Pathway.
The AMPK signaling pathway is a master regulator of cellular energy homeostasis and metabolism AMPK is regulated by diverse mechanisms and stimuli that provide a variety of opportunities for pharmacological intervention. (A) Indirect Activation: Upstream AMPK activators. LKB1 and CaMKKβ principally regulate AMPK. Stimulation of these pathways upstream of AMPK can activate AMPK signaling indirectly. (B) Direct AMPK Activators. AMPK can be directly activated by a nucleotide analog (such as AMP and ZMP) binding to the regulatory subunit and inducing a conformational change that enhances AMPK phosphorylation. (C) Downstream AMPK signaling pathways. The AMPK pathway can also be activated by stimulation of downstream signaling partners. This can mimic and/or enhance the effects of AMPK activation in response to normal physiological stimuli. (D) Indirect inducers of metabolic stress. Many compounds and stimuli induce metabolic stress, which results in the release of Ca2+ ions, and fluctuation in the cellular AMP/ATP ratios. These metabolites play a profound role in regulation of AMPK activation and can significantly enhance AMPK signaling under these conditions. (E) miRNA modulation of AMPK pathway. The AMPK pathway is the target of multiple miRNAs, which regulate the expression of key regulators in the pathway. Changes in miRNA expression resulting from pharmacological intervention or changes in blood glucose levels can release the suppression on the system resulting in enhance AMPK expression and activation.