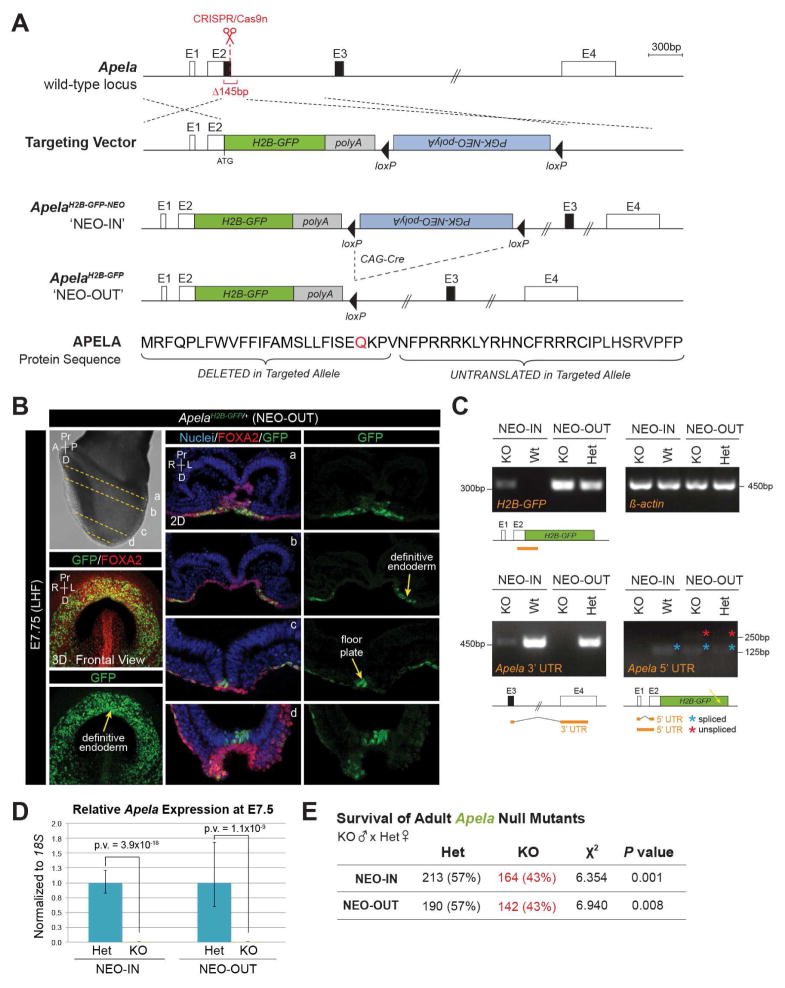
FIGURE 1. Apela null mice generated by H2B-GFP-pA knock-in have reduced survival.
(A) Targeting of the Apela locus. Untranslated (white boxes) and coding (black boxes) sequence. Homology directed repair deleted 145bp. Elements are to scale except where indicated (double hash). Modification of Apela protein sequence by gene targeting (signal peptide cleavage site, red). E, Exon. (B) Immunostaining for GFP and FOXA2 (LHF, late headfold). 3D MIP frontal views (left) and 2D sections (a–d). Nuclei are stained with Hoechst. (C) Amplification of Apela transcript fragments (orange lines) from embryos by RT-PCR. Spliced (blue asterisk) and unspliced (red asterisk) 5′ UTR products. H2B-GFP transcripts were amplified from NEO-IN embryos, but may be unstable or insufficient for protein detection. (D) Expression of Apela by qRT-PCR. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (E) Chi squared analysis of recovered Apela genotypes from homozygous null males crossed to heterozygous females.