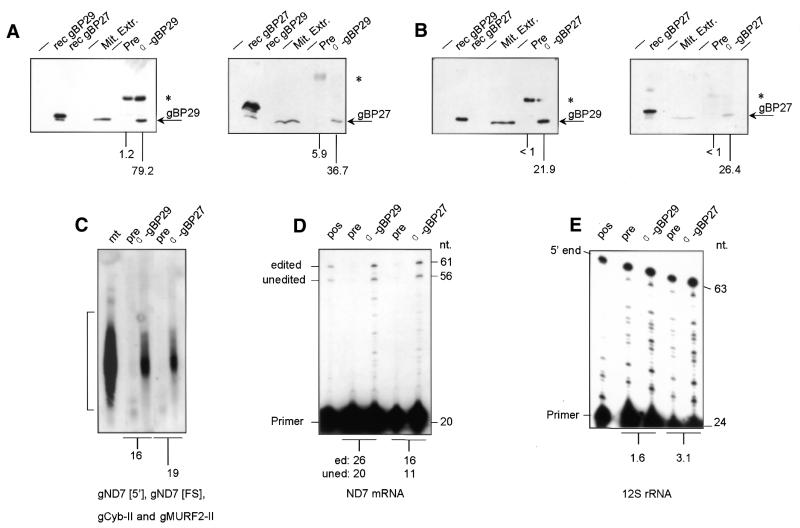
Figure 8.
Co-immunoprecipitation analysis. (A and B) Mt extracts of C.fasciculata were incubated with Staph A coated with α-gBP29 serum (A), α-gBP27 serum (B) or pre-immune serum (Pre) (A and B), followed by washing and centrifugation as described in Materials and Methods. Immunoprecipitates were analysed for the presence of either gBP29 (left-hand panels) or gBP27 (right-hand panels) by PAGE and western blotting. In addition, 8 ng E.coli extracts expressing either gBP29 (rec gBP29) or gBP27 (rec gBP27) and the mt extract used as starting material for the immunoprecipitation reaction (Mit. Extr.) were applied to the PAGE gel. Arrows indicate the positions of gBP29 and gBP27; asterisks mark the positions of IgG heavy chains that are occasionally visible. The numbers under the lanes indicate the amounts of gBP29 or gBP27 found in the immunoprecipitate, as a percentage of the total amount present in the mt extract used in the experiment. (C–E) Immunoprecipitates obtained with pre-immune serum (pre), α-gBP29 antibodies and α-gBP27 antibodies were tested for the presence of gND7[FS], gND7[5′], gCyb-II and gMURF2-II by northern blot analysis (C), the presence of ND7 mRNA (edited or unedited at the frameshift position) (D) and 12S rRNA (E) by primer extension analysis. The position of the radiolabelled oligonucleotide (primer) used in the extension reaction is indicated, as is that of the extension products. Primer extension was carried out in the presence of ddGTP instead of dGTP, resulting in a product of 61 nt derived from ND7 RNA edited by insertion of five U residues at the frameshift position and a 56 nt fragment derived from unedited ND7 RNA. Pos., positive control of the primer extension reaction with C.fasciculata total RNA. The numbers under (C)–(E) indicate the ratios of the amounts of RNA present in the immunoprecipitates generated with α-gBP29 and α-gBP27, respectively, and those generated with pre-immune serum.