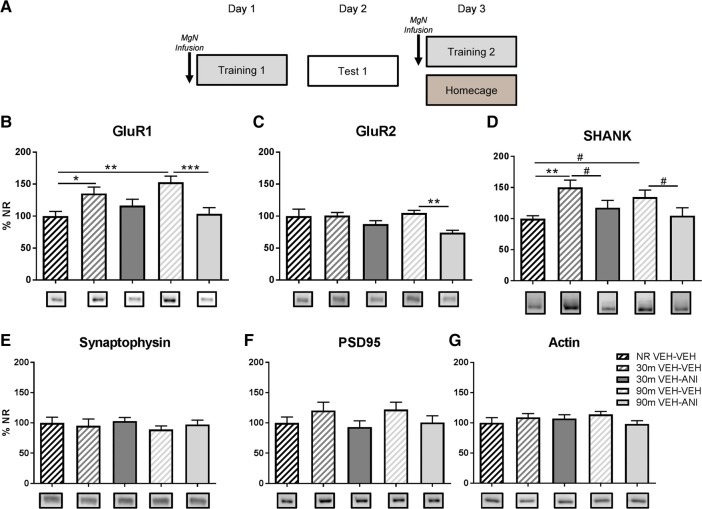
Figure 3.
MgN protein synthesis is critical for changes in amygdala synaptic expression of AMPA receptors underlying the change from low to high fear generalization. (A) Rats were infused with vehicle (ACSF) 30-min before the first training session using random presentations of CS+–UCS and CS− cues using a 0.5 mA footshock followed by a test 24-h after the first training session. Rats received a second infusion of either vehicle or anisomycin 30-min prior to the second training session using a 1.0 mA footshock and were sacrificed 30 or 90 min following training. Animals that did not receive a second training session were infused with vehicle and placed back into their homecages for the duration of the training session and were sacrificed 90-min later (n = 6–9). (B,D) The second training session is characterized by increased amygdala GluR1 and SHANK synaptic expression that is prevented with infusion of anisomycin into the MgN. (C) Anisomycin infusions into the MgN reduced the amount of GluR2 in synaptosomal fractions. (E–G) Expression of synaptophysin, PSD95, and β-actin were not changed due to training or drug infusion. (#) P < 0.07, (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01, (***) P < 0.001.