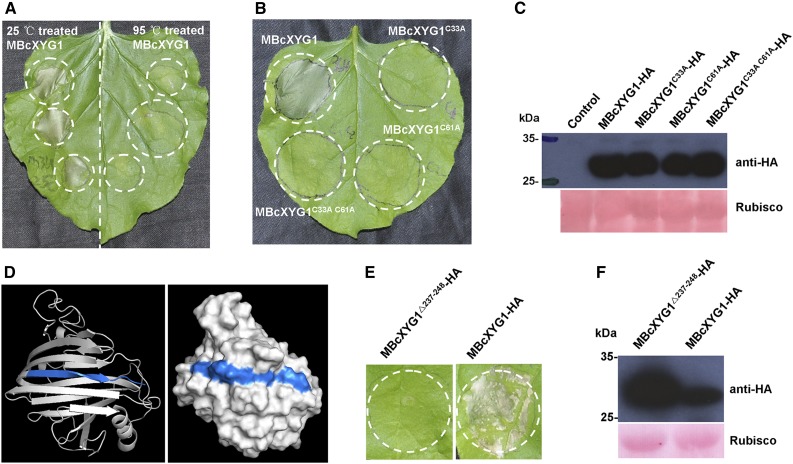
Figure 7.
The necrosis-inducing activity of BcXYG1 is dependent on the protein tertiary structure. A, Assessment of the activity of denatured BcXYG1. Purified MBcXYG1 protein was incubated for 15 min at 25°C or 95°C. N. benthamiana leaves were treated with 100 μg mL−1 native (left) or denatured (right) proteins. Photographs were taken 5 d after the treatment of leaves. B, Assessment of the effect of destabilization of the tertiary structure on the activity BcXYG1. N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens strains expressing constructs of MBcXYG1 with mutations that destroy the tertiary structure of the protein. Photographs were taken 5 d after treatment. MBcXYG1C33A-HA, Mutation in Cys residue 33; MBcXYG1C61A-HA, mutation in Cys residue 61; MBcXYG1C33A C61A-HA, mutation in both Cys residues 33 and 61. C, Immunoblot analysis of proteins from N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing Cys residue mutants BcXYG1C33A-HA, BcXYG1C61A-HA, and BcXYG1C33A C61A-HA from a pCAMBIA3300 vector. HA-tagged proteins were detected using anti-HA antibodies, Ponceau S-stained blots show the Rubisco large subunit. D, 3D structural models of BcXYG1 predicted using I-TASSER (http://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/I-TASSER/) and analyzed further by PyMOL software. Left, Cartoon model of BcXYG1; right, surface model of BcXYG1. The 12 C-terminal amino acids constituting a β-strand structure (VFKTTAYSVSLN; amino acids 237–248) are depicted in blue. E, Effects of the destabilization of BcxYG1 by deletion of the 12 C-terminal amino acids. Photographs were taken 5 d after infiltration with an A. tumefaciens strain expressing either the mutant protein MBcXYG119-236(Δ237-248)-HA (left) or a native form of MBcXYG1 (right). F, Immunoblot analysis of proteins from N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing either the 12 C-terminal amino acid deletion mutant MBcXYG119-236(Δ237-248)-HA or MBcXYG1.