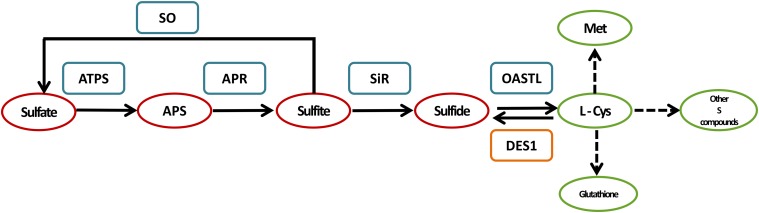
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the Sulfate reduction and Cys degradation pathways in Arabidopsis plants. ATPS catalyzes the adenylation of sulfate to APS using ATP as an electron donor. Then, APS is reduced by the plastidic enzyme APR to sulfite in the presence of two molecules of reduced GSH, which acts as an electron donor. The generated sulfite can be oxidized to sulfate by SO with the formation of H2O2 as a byproduct or further be reduced to sulfide by the SiR employing three molecules of reduced ferredoxin. The sulfide together with O-acetyl-l-Ser is the substrate for Cys biosynthesis catalyzed by OAS-TL. Cys homeostasis is controlled by l-Cys desulfhydrase (DES1, EC 4.4.1.1), which catalyzes the breakdown of Cys to sulfide, ammonia, and pyruvate. Red circle, inorganic S compounds; green circle, organic S compounds; blue rectangle, sulfate reduction pathway enzymes; orange rectangle, Cys degradation pathway enzyme.