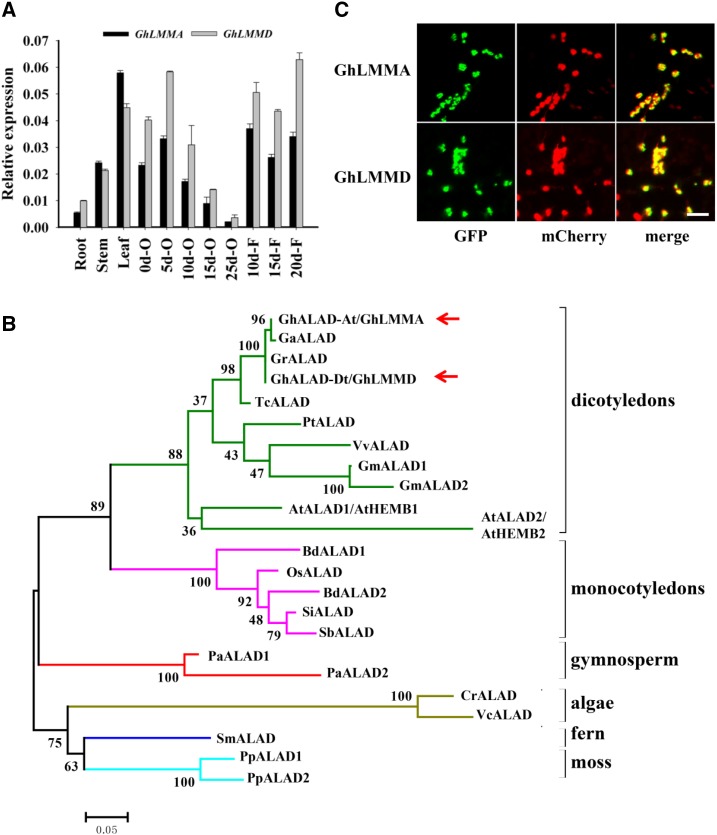
Figure 2.
Characterization of GhLMMD. A, Transcript abundance of GhLMMA (GhLMM in A subgenome) and GhLMMD (GhLMM in D subgenome) in different tissues of G. hirsutum acc. TM-1 quantified by qRT-PCR using gene-specific primers. GhLMMA and GhLMMD showed similar expressions in tested cotton tissues, with higher expression levels in leaves, early stage ovules, and developmental fibers. B, Phylogenetic analysis of the GhLMM orthologs (ALAD genes) in different species. Twenty-three ALAD proteins from 17 species, including algae, ferns, moss, gymnosperms, and angiosperms, were used to construct the phylogenetic tree. Species analyzed included algae (Cr: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Vc: Volvox carteri), fern (Sm: Selaginella moellendorffii), moss (Pp: Physcomitrella patens), gymnosperm (Pa: Picea abies), monocotyledons (Si: Setaria italic; Sb: Sorghum bicolor; Bd: Brachypodium distachyon; Os: Oryza sativa), and dicotyledons (Tc: Theobroma cacao; Gh: Gossypium hirsutum; Gr: Gossypium raimondii; Ga: Gossypium arboreum; At: Arabidopsis thaliana; Pt: Populus trichocarpa; Vv: Vitis vinifera; Gm: Glycine max). Red arrows indicate GhLMMA and GhLMMD. C, Chloroplast localization of GhLMM. GhLMMA and GhLMMD were respectively fused with GFP and transiently expressed in tobacco epidermal cells by Agro-infiltration. Chloroplast localized Rubisco protein fused with mCherry was used as positive control. GhLMM-GFP fusion proteins colocalize with Rubisco-mCherry fusion and show yellow signals after merging. Bars = 20 μm.