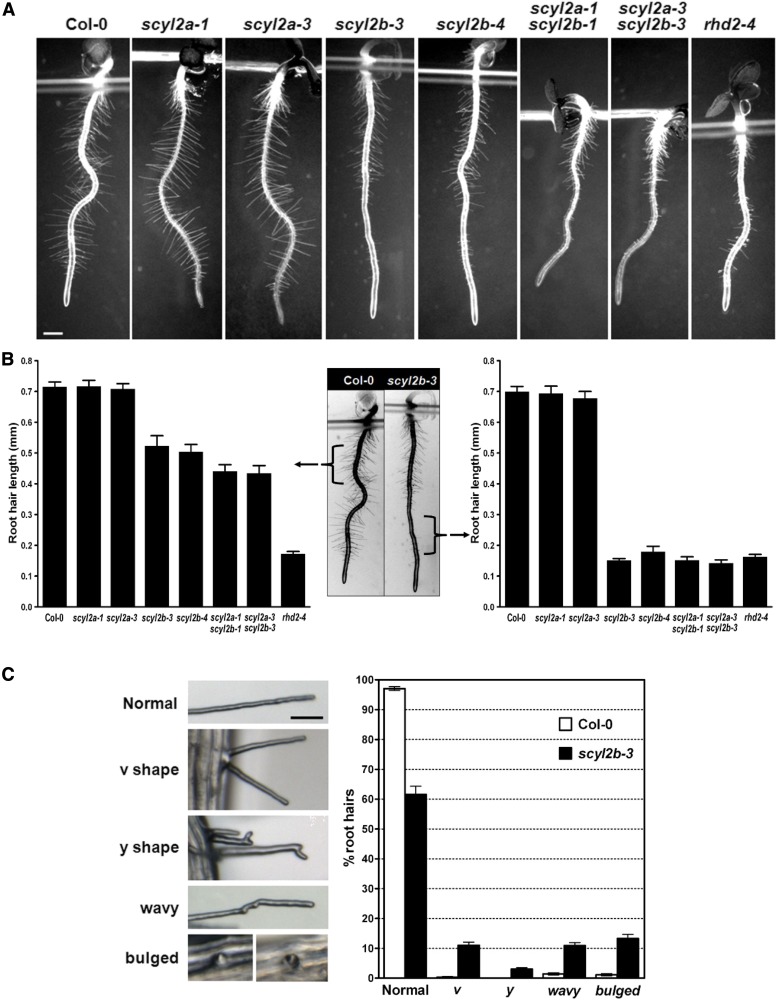
Figure 3.
SCYL2B functions in root hair development. A, Light microscopy images showing root hair length of wild-type Col-0, scyl2a, scyl2b, and scyl2a scyl2b double mutant alleles. Three-day-old roots were used for the measurement of root hair length in A and B. Bar = 0.5 mm. B, Root hair length of seedlings of wild-type Col-0, scyl2a, scyl2b, and scyl2a scyl2b double mutant alleles. Root hair length was measured in two separate regions of root: the 2-mm region below hypocotyls (left graph and middle image) and the 2-mm region starting 0.5 mm above the root hair differentiation zone (right graph and middle image). Fifteen root hairs per each seedling were measured, and 10 seedlings per genotype were used for root hair length measurements (n = 10 seedlings; means ± se). C, Abnormal root hairs in scyl2b-3. Root hairs in scyl2b-3 were classified into five classes based on their phenotype (normal, v shape, y shape, wavy, and bulged). Representative images of each class are shown (left). Percentages of each root hair class were determined in wild-type Col-0 plants and scyl2b-3 (right). About 70 to 100 root hairs per each seedling were counted in 5-mm regions starting 0.5 mm above the root hair differentiation zone (n = 10 seedlings; means ± se). At least two independent experiments were performed.