Figure 4. Characterization of representative IE, E and L antigen-specific CD8+ T cell clones.
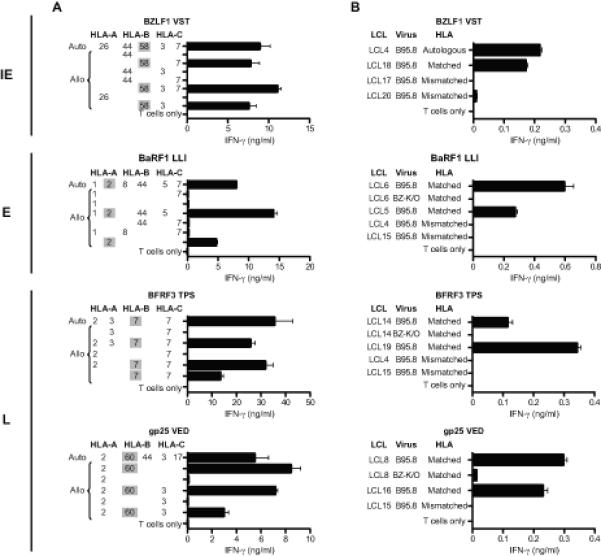
Recognition of target LCLs was measured by IFN-γ ELISA and results are mean ± 1 SD of duplicate wells. (A) HLA restriction of CD8+ T cell clones. T cells were incubated overnight with peptide-loaded cells of the autologous B95.8 LCL and of partially HLA class I-matched allogeneic LCLs (for which the matching alleles are given). (B) CD8+ T cell recognition of unmanipulated LCL targets. T cells were incubated overnight with LCL cells from HLA-matched (or autologous) and HLA-mismatched donors. Where possible, a pair of B95.8 and BZ-K/O LCLs from an HLA-matched donor was included. All HLA-matched B95.8 and BZ-K/O LCLs were strongly recognised by the relevant T cells if they were pre-exposed to target peptide, with > 8ng/ml IFN-γ released in all cases (data not shown). N.B. Levels of B95.8 LCL recognition by IE versus E versus L antigen-specific clones cannot be directly compared since the percentage of lytically-infected cells in these LCLs differs between cell lines.
