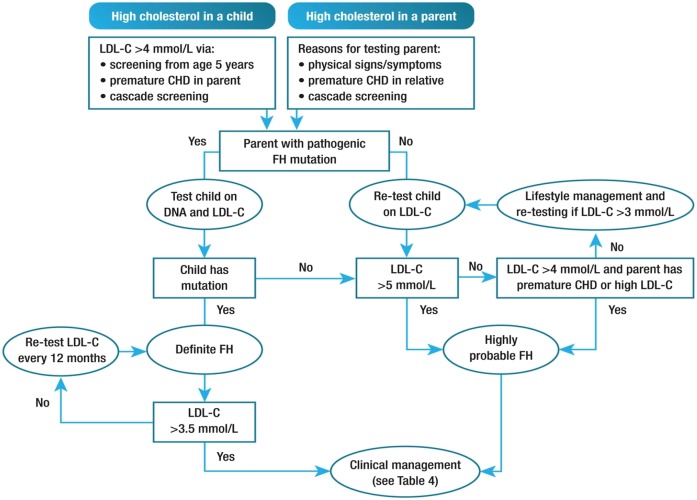
Fig. 3.
Potential strategy for diagnosis of FH in children and adolescents. Premature CHD is defined as a coronary event before age 55 years in men and age 60 years in women. Definite FH is defined as genetic confirmation of at least one FH-causing genetic mutation. Close relative is defined as first or second degree. Highly probable FH is based on clinical presentation (i.e., phenotypic FH), either an elevated LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) level ≥5 mmol/l in a child after dietary intervention or an LDL cholesterol level ≥4 mmol/l in a child with a family history of premature CHD in close relatives and/or baseline high cholesterol in one parent. Cascade screening from an index case with a FH-causing mutation may identify a child with elevated LDL cholesterol levels ≥3.5 mmol/l. Reproduced from Wiegman et al. (25).