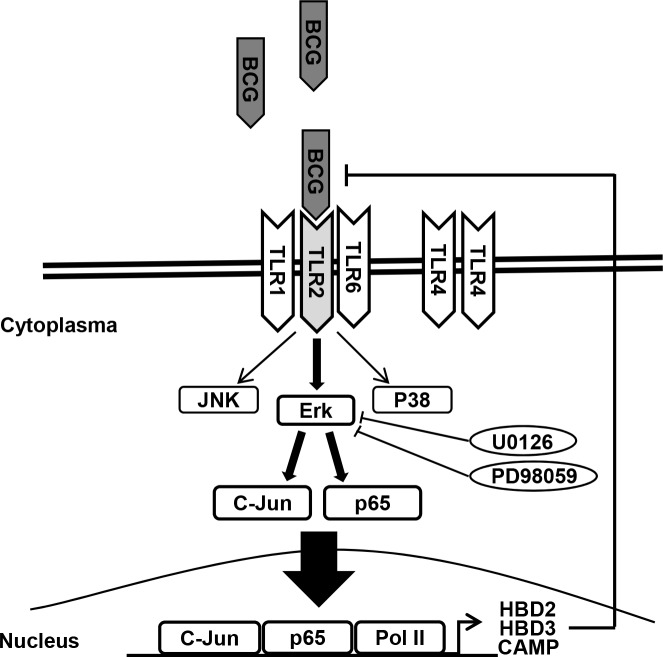
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the working hypothesis.
BCG induces ERK phosphorylation via TLR 2, leading to c-Jun- and p65-dependent transcription of HBD2, HBD3, and CAMP. Pharmacological inhibition of ERK phosphorylation and/or genetic ablation of TLR2 enhance the anti-proliferative effects of BCG on bladder cancer cells.