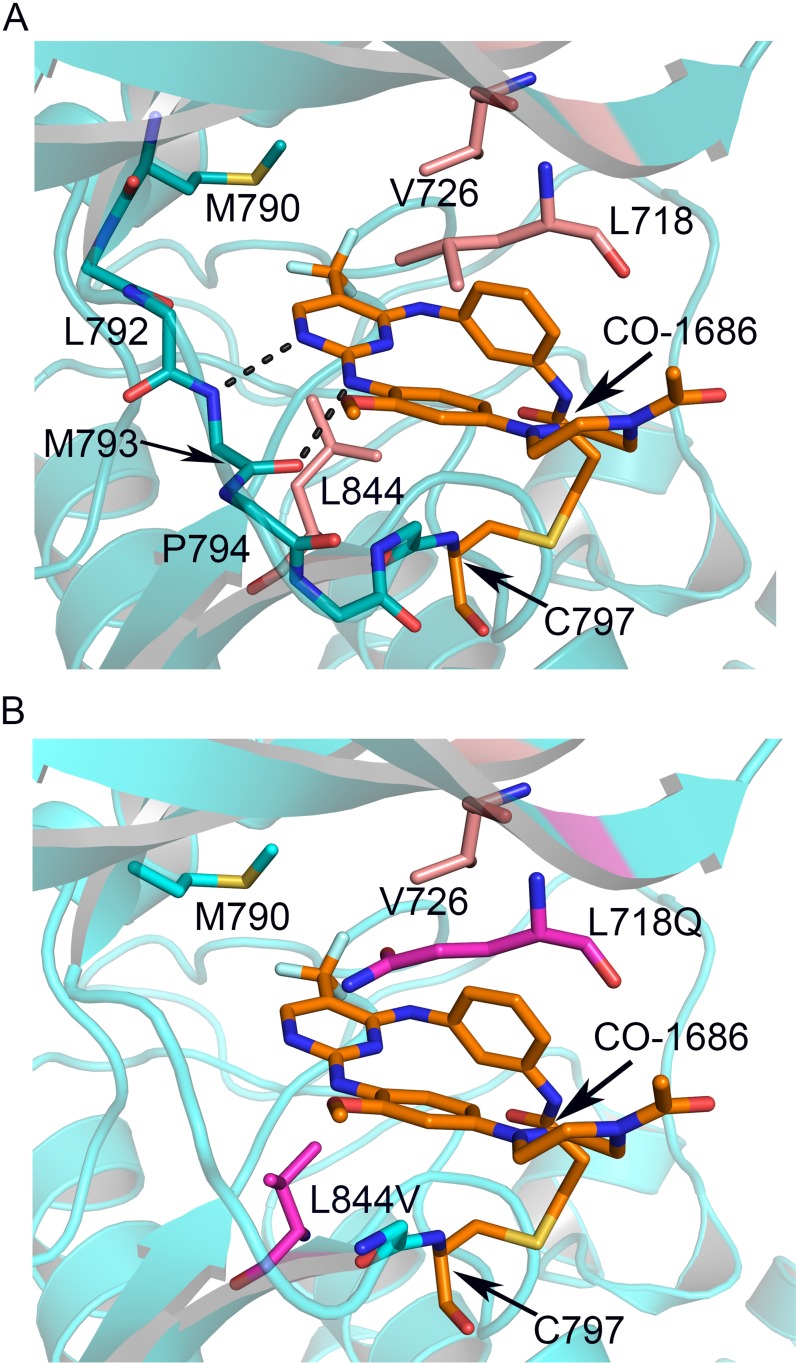
Figure 3. Interactions between CO-1686 and EGFR and the structural basis of drug-resistance conferred by L718Q and L844V.
(A) Crystal structure of CO-1686 in complex with EGFR T790M. The EGFR kinase is shown as cartoons in cyan, and the bound CO-1686 is shown as sticks in orange. The amide and carbonyl atoms of Met793 interact with the aminopyrimidine of CO-1686 through hydrogen bonds shown by dashed lines. Residues contacting CO-1686 are shown as sticks. (B) Structural modeling illustrating the influences of EGFR L718Q and L844V mutations to the interactions with CO-1686. The L718Q mutation (carmine) is predicted to hinder the binding of CO-1686 owing to steric hindrance and/or abolishment of hydrophobic interaction, while the shorter side chain of L844V (carmine) will weaken the hydrophobic interaction with the pyrimidine core of CO-1686.