Abstract
SUMMARIZING THE IMPORTANCE OF THE STUDY
The repetitive usage of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) is critical for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluation of tumor burden in glioblastoma patients. It is also a crucial tool for determination of radiographical response to treatment. GBCA injection, however, comes with a 2.4% rate of adverse events including life-threatening conditions such as nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF). Moreover, GBCA have been shown to be deposited in brain tissue of patients even with an intact blood-brain barrier (BBB). The present study explores quantitative T1 relaxometry as an alternative non-invasive imaging technique detection of tumor burden and determination of radiographical response. This technique exploits specific properties of brain tissue with impaired BBB. With a sensitivity and specificity as high as 86% and 80%, respectively, quantitative T1-relaxometry allows for detecting contrast-enhancing areas without the use of GBCA. This method could make it unnecessary to subject patients to the risk of adverse events associated with the use of GBCA. Nonetheless, a large-scale analysis is needed to confirm our findings.
Background
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) are crucial for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based evaluation of tumor burden in glioblastoma (GBM). Serious adverse events of GBCA, even though uncommon, and gadolinium deposition in brain tissue could be avoided by novel imaging techniques not requiring GBCA. Altered tissue composition in areas with impaired blood-brain-barrier also alters the quantified T1 relaxation time (qT1), so that qT1 analysis could replace GBCA-based MRI for the analysis of tumor burden and response.
Methods
As a part of a prospective pilot MRI-relaxometry trial, patients with newly-diagnosed GBM who relapsed under standard radiochemotherapy were selected for this study. At recurrence, subtraction of qT1 maps pre and post-GBCA application (ΔqT1 maps) was used to determine areas of contrast-enhancement. With the contrast-enhancement on ΔqT1 maps as reference, ROC analysis served to detect an optimal qT1 cut-off on qT1 maps prior to GBCA to distinguish between contrast-enhancing tissue and its surroundings.
Results
Ten patients were included. A qT1 value >2051ms predicted contrast-enhancing tumor tissue with a sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 80% (AUC, 0.92; p<0.0001). Interestingly, qT1 prolongation >2051 ms that did not overlap with contrast-enhancing area transformed into contrast-enhancement later on (n=4).
Conclusion
T1-relaxometry may be a useful technique to assess tissue properties equivalent to contrast-enhancement without the need for GBCA application. It may also provide information on sites with future tumor progression. Nonetheless, large-scale studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: T1-mapping, quantitative MRI, BBB damage, glioblastoma, T1-relaxometry
INTRODUCTION
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uncovers impaired blood-brain barrier (BBB) associated with aggressive features of glioblastoma and is therefore widely used in the diagnosis and monitoring of this highly malignant brain tumor. A significant increase of the contrast-enhancing area is the most relevant criterion for diagnosing tumor progression and may indicate a need to switch therapy [1–3]. MRI contrast agents used for monitoring tumor burden of glioblastoma patients are based on gadolinium (GBCA). Apart from the discomfort for the patient prompted by the intravenous injection itself, prolonged scanning time, and additional costs, severe adverse events have been observed with GBCA usage. Adverse events upon GBCA application are uncommon with a frequency of 2.4% [4]. However, some of them, such as the nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) might impede GBCA usage especially in patients with renal failure, which are particularly prone to gadolinium-induced NSF [4]. Further, recent studies reported gadolinium deposition in the brain in patients receiving repetitive GBCA injections [5], even in individuals with intact BBB. Last but not least, gadolinium has a negative environmental impact, it is a costly rare earth metal with limited natural resources while its use and consequent excretion contaminates water [5–7]. Limiting GBCA usage would therefore be advisable but GBCA are particularly important in patients with diseases like glioblastoma who need repetitive GBCA-based MR examinations. For these patients, GBCA-independent new imaging techniques need be developed.
In the brain, the water content is strictly regulated by the BBB that preserves the central nervous system homeostasis. In MRI, the T1-relaxation time is a basic physical value which is substantially influenced by the content of interstitial tissue water [8–10]. When the tumoral BBB is damaged, water and paramagnetic gadolinium (Gd) complexes may pass into the perivascular tissue, allowing thermodynamic interaction with their surroundings, the lattice. The spin-lattice relaxation time, also known as T1, decreases when proteins and Gd complexes accumulate but increases when only water accumulates [11–13]. While Gd complexes are too large to diffuse over long distances outside the tumor tissue, water diffuses far beyond the tumor tissue and results in peritumoral edema mainly along white matter tracts [14]. Increased tissue water results in T1-prolongation in glioblastoma tissue and its surrounding edema [12, 13]. However, different composition of the lattice according to the presence of tissue water should result in different T1 values. QT1 mapping is a quantitative method that enables estimation of the interstitial water content [15, 16].
We suggest that there is a threshold of T1-increase in pre-contrast images that indicates the presence of enhancing tumor tissue and discriminates it from non-enhancing peritumoral area and from normal brain tissue. To evaluate this hypothesis, we measured T1 in patients with histologically proven glioblastoma (GBM) pre- and post-injection of GBCA. Areas with significant T1 shortening post-GBCA served to detect contrast-enhancing tumor tissue. Comparing pre-GBCA T1 in the so obtained contrast-enhancing tumor tissue against pre-GBCA T1 in the surrounding tissue served to determine a potential cut-off value for discriminating tumor tissue from peritumoral edema and normal brain tissue.
RESULTS
Subjects
Ten patients were eligible for inclusion in this pilot study. The corresponding patients’ characteristics are provided in Table 1.
Table 1. Patients’ and tumor characteristics.
| Pt. no. | Sex | Age1 | First-Line Treatment | MGMT | TP | Extent of overlap between area with qT1 >2051 ms and enhancing tumor | Extent of non-overlapping area with qT1 > 2051 ms later transforming to enhancing tumor5 | qT1 (ms) | TP of progression (RANO) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f | 53 | RT*+TMZ, TTF, D | - | TP9 | excellent | completely | 2481 | |
| TP10 | excellent | completely | 2482 | ||||||
| TP11 | motion artifacts | 2250 | TP11 | ||||||
| 2 | f | 58 | B, RT+TMZ | + | TP1 | excellent | none | 2158 | |
| TP2 | excellent | completely | 2676 | ||||||
| TP3 | excellent | 2605 | TP3 | ||||||
| 3 | f | 62 | pR, RT+TMZ | - | TP4 | excellent | none | 2772 | |
| TP5 | moderate | none | 2598 | ||||||
| TP6 | moderate | 2083 | TP 6; necrotic tumor | ||||||
| 4 | m | 67 | pR, RT+TMZ | - | TP2 | moderate | partially (80%) | 2615 | |
| TP3 | excellent | partially (60%) | 3051 | ||||||
| TP4 | excellent | 3091 | TP4 | ||||||
| 5 | m | 74 | pR, RT+TMZ, D | + | TP0 | excellent | completely | 2076 | |
| TP1 | excellent | completely | 2227 | ||||||
| TP2 | excellent | 3631 | TP2 | ||||||
| 6 | m | 58 | B, TR+TMZ | - | TP2 | excellent | partially (90%) | 2804 | |
| TP4 | excellent | none | 2776 | ||||||
| TP5 | excellent | 2955 | TP5 | ||||||
| 72 | m | 60 | cR, RT+TMZ | - | TP3 | excellent | none | 2911 | |
| TP4 | excellent | none | 3088 | ||||||
| TP5 | excellent | 2743 | TP6 | ||||||
| 8 | f | 72 | cR, RT, TP3: TMZ | + | TP3 | excellent | none | 1994 | |
| TP4 | excellent | none | 2705 | ||||||
| TP5 | moderate4 | 1962 | TP5 | ||||||
| 9 | f | 69 | pR, RT+TMZ | - | TP2 | moderate | none | 2516 | |
| TP3 | moderate | none | 2928 | decreased enhancement | |||||
| TP4 | poor | 1842 | TP4; necrotic tumor | ||||||
| 103 | n | 47 | cR, RT+TMZ, adjuvant CCNU+TMZ | + | TP7 | poor | none | 1873 | |
| TP8 | poor | none | 1660 | ||||||
| TP9 | poor | 1517 | TP9; re-surgery: pseudo-progression |
1, Age at first glioblastoma surgery; 2, gliosarcoma; 3, glioblastoma with oligodendroglial component; 4, T1 non-prolonged area regressed at TP6; 5, extent of area with qT1 > 2051ms that does not overlap with contrast-enhancing area, which transforms to enhancing tumor on a later follow-up
f, female; m, male; MGMT, O6-Methyl-Guanin-Methyl-DNA-Transferase promoter methylation; +, methylated; -, not methylated; TP, time point; B, stereotactic biopsy; cR, complete resection; pR, partial resection; RT, radiation therapy with 60 Gy; RT*, radiation therapy with 22 Gy; TTF, treatment with tumor treating fields; TMZ, temozolomide; RT+TMZ, combined radiochemotherapy with TMZ followed by adjuvant TMZ; CCNU, chloroethyl-cyclohexyl-nitrosourea; D, dexamethasone treatment as of surgery
Defining a cut-off value for pre-GBCA qT1
ROC analysis (Figure 1) revealed that a pre-GBCA qT1 value of >2051 ms discriminated best between the contrast-enhancing tumor on ΔqT1 maps and the surrounding tissue. Pre-GBCA qT1 values above 2051 ms predicted true tumor tissue with a sensitivity of 86% (95% confidence interval (CI), 78 – 92%) and a specificity of 80% (CI, 71 - 87%). The area under the ROC curve (Figure 1) was 92% ± 1.8% standard deviation (SD) (CI, 89 - 95%; p<0.0001).
Figure 1. ROC curve.
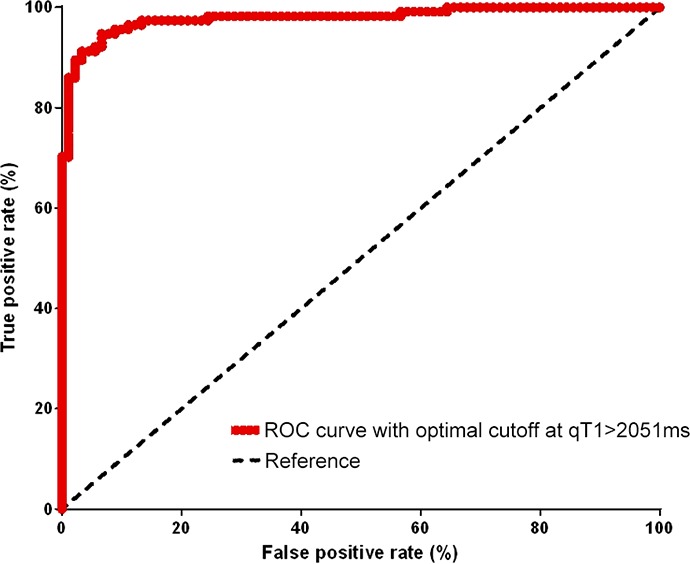
This plot shows qT1 values [ms] at different cutoffs and quantifies their the sensitivity and specificity in discriminating the solid contrast-enhancing tumor from the surroundings. The optimal performance is reached at a qT1 value of 2051ms.
Overlap between areas with elevated pre-GBCA qT1 and contrast-enhancing tumor
The overlap between areas with pre-GBCA qT1 >2051 ms (qT1-prolonged area) and the contrast-enhancing tumor on ΔqT1 maps (gold standard) was on average 85% across all time-points and patients (Table 1). We observed a varying extent of overlap, which was subdivided in three major extent of overlap classes: excellent (≥ 90%), moderate (50-89%) and poor overlap (0-49%).
An excellent overlap was observed at least one of three evaluated time-points in eight patients. Moreover, seven patients showed even an excellent overlap at two or more time-points (Table 1, patients 1,2,4,5,6,7,8). As an example, Figure 2 shows the qT1 maps of one of those patients (Table 1, patient 2).
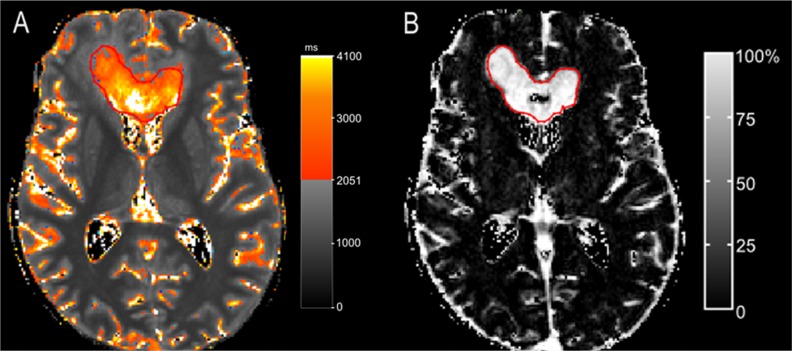
Figure 2. A patient with >90% overlap (patient 2).
The color map (A) shows areas with pre-GBCA qT1 > 2051 ms, delineated by a red line as a gradient between red and yellow. A nearly complete overlap is seen at time-point of progression between pre-GBCA qT1 (A) and the contrast-enhancing tumor on the subtraction map ΔT1, which is outlined in red (pre-GBCA qT1 – post-GBCA qT1) (B).
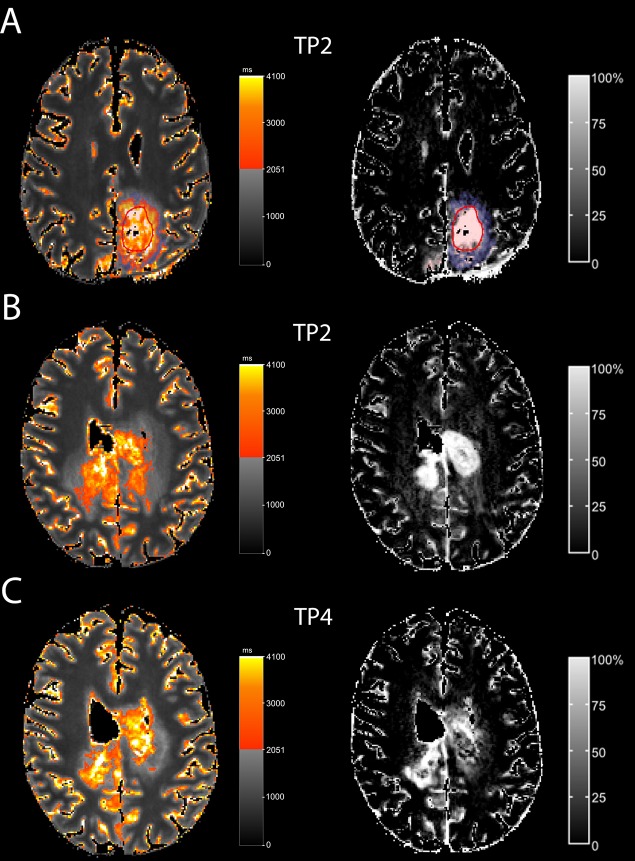
A moderate overlap was found at least one time-point in four patients (Table 1, patients 3,4,8,9). A predominantly moderate overlap, i.e. a moderate overlap at least 2 of 3 time-points, however, was only seen in two patients (Table 1, patients 3,9). As evidenced by the respective ΔqT1 maps (gold standard), those two patients had mainly necrotic tumors at the time of progression. In one patient (Table 1, patient 9), the contrast-enhancing area, which did not overlap with the qT1-prolonged area, regressed at the next MRI timepoint, whereas the overlapping contrast-enhancing tumor progressed (Figure 3).
Figure 3. A patient with moderate overlap (patient 9).
A Quantitative map with a subtraction map qT1 at time-point TP 5) (A) and conventional MRI at TP 5 and TP 6 (B) of a 70-year-old woman with recurrent GBM. At TP 5, the quantitative map (A, on the left-hand side) shows pre-GBCA qT1 area with >2051 ms (red to yellow, green arrows) with a good overlap of the dorsal contrast-enhancing tumor seen on the subtraction map ΔT1 (A, on the right-hand side), but the second smaller contrast-enhancing tumor area (crosshair) is missing on the color map. This contrast-enhancing area without overlap (crosshair) regressed in the next conventional MRI (TP 6) (B), whereas the contrast-enhancing tumor with overlap progressed. Also, note additional area of T1-prolongation outside the contrast-enhancing tumor.
A poor overlap could be demonstrated at least one time-point in two patients (Table 1, patients 9 and 10). In one of those patients (Table 1, patient 10), the contrast-enhancing area had 0% to maximally 10% overlap with the qT1-prolonged area. This patient had progressive disease according to RANO and underwent re-surgery that revealed mainly therapy-induced tissue changes and only very scattered tumor cells so that these changes were classified as pseudoprogression.
Predictive role of qT1-prolonged areas for tumor recurrence
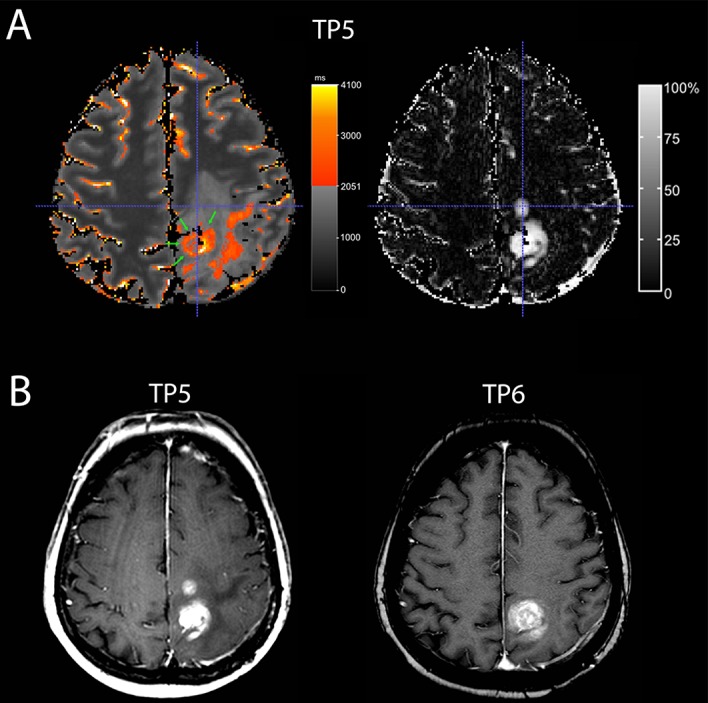
In five patients (Table 1, patients 2,3,7,8,9), the qT1-prolonged area was restricted to the contrast-enhancing tumor. In the remaining five patients, the qT1-prolonged area extended beyond the contrast-enhancing tumor (Figure 3 and 4 show this in exemplary fashion for patients 5 and 6). The qT1-prolonged area outside the contrast-enhancing tumor partially matched the subtle contrast-enhancement surrounding the solid contrast-enhancement (Figure 4A shows this in exemplary fashion for patient 5). Small parts of these areas transformed to contrast-enhancing tumor at the time of progression in four patients (Patients 1,4,5,6) (Figure 4B and 4C show this in exemplary fashion for patient 6), or at a later timepoint (n=1, patient 4). Interestingly, three of the five patients (Patients 1,4,5) with the qT1-prolonged area outside the contrast-enhancing tumor had prior partial resection or biopsy with substantial remaining tumor burden.
Figure 4. T1-prolongation > 2051 ms outside the solid contrast-enhancing tumor.
In one patient (A; patient 5), T1-prolongation >2051 ms outside the solid contrast-enhancing tumor (red circle) partially fitted with the subtle enhancement (ΔqT1, blue). In another patient (B, C; pat 6), T1-prolongation >2051 ms outside the solid contrast-enhancing tumor at TP 2 (B) partially matched subtle enhancement (ΔqT1). At TP4 (C), this area transformed to contrast-enhancing tumor.
DISCUSSION
This work shows that the quantitative relaxation time T1, qT1, is markedly increased in contrast-enhancing areas of glioblastoma. On pre-GBCA maps, areas with qT1 >2051 ms predicted the contrast-enhancing tumor with a good diagnostic performance. Thus, without the need for GBCA application, the tumor may probably be made visible on pre-GBCA maps by identifying areas with a qT1 increase above 2051 ms. Consequently, qT1 maps might be a useful tool to visualize and monitor tumor growth without using a contrast agent. This might be particularly important in preventing contrast agent induced adverse events.
In the present study, we observed high values of qT1 in the contrast-enhancing tumor. T1-relaxation time is known to increase when water accumulates in the absence of Gd complexes [11–13]. There may be two major reasons for this finding. First, tumor tissue consists of tumor cells, activated glia cells, tumor vessels, and micro-necrosis, which all interact to a very small degree with the spins of water molecules and thus result in high T1 values [17, 18]. Second, the immediate vicinity of contrast-enhancing tumor to leaky tumor vessels leads to a high water content and thereby high T1 [19]. Our findings are in line with previous reports of increased T1 in brain tumors [20–22].
In contrast, T1 prolongation in peritumoral edema is less pronounced because peritumoral edema mainly extends along the white matter tracts, which are known for a high protein and fat content [23]. These properties allow for qT1 to be used as a discriminator between true tumor tissue and peritumoral edema.
Studies carried out in the 1990s found more variable T1 values in glioblastoma tissue as compared to our data [24, 25]. Beside technical and methodical advances, our results differ from those of previous studies in that we only analyzed T1 in the contrast-enhancing part of the tumor, which was semi-automatically segmented on ΔqT1 maps. ΔqT1 maps that were calculated on the grounds of quantitative T1 values pre- and post-GBCA, allowed us to exclude macroscopically visible necrotic areas, which contain various elements such as hemorrhages and protein-rich exudates that shorten T1 values.
Another major finding of this study is that areas with qT1 values lower than 2051 ms may represent pseudoprogression instead of true tumor progression. Although we aimed to include only patients with unequivocal tumor progression according to RANO, there was one patient with late tumor-imitating therapy-induced changes, confirmed via biopsy, and one patient with partial regression of the contrast-enhancing areas. In both patients, qT1 values were below 2051 ms. This shows that classification by RANO may not always be suited to differentiate between pseudoprogression and true tumor progression. QT1 measurements may be superior in this regard.
Color-coded visualization of areas with qT1 increase >2051 ms did not show satisfactory results in all patients. In patients with predominantly necrotic tumor, the necrotic area hardly overlapped with the contrast-enhancing tumor. In these patients, areas of contrast-enhancing tumor were missed on pre-GBCA qT1 maps based on a qT1 cut-off value of 2051ms. In addition, patients with substantial tumor burden also exhibited qT1-prolongation outside the contrast-enhancing tumor. The biological value of these areas remains questionable because only smaller parts of these areas transformed into tumor later on. A putative explanation for the low qT1 values observed in the necrotic area might be the elevated protein and lipid content present in necrotic tissue [26], which is usually accompanied by decreased qT1. A comparison of areas with decreased qT1 with the respective histological phenotype should be included in future studies to help explain our observations.
A major limitation of this pilot study is the small sample size. Thus, statistical interpretation is restricted and our findings need to be corroborated in an independent trial with a larger sample size. In addition, translation into clinical application has several limitations: First, the longer measurement times of quantitative MRI and, to avoid missing the critical time-point of tumor progression, short time intervals of 6 weeks were only tolerable for a limited number of patients. Second, this pilot study included patients after surgery and during therapy. Therefore, the contrast-enhancing areas observed on ΔqT1 maps may reflect therapy-induced changes to some extent. To account for this issue, we only included patients with progressive disease and included the evaluation of qT1 maps before the time-point of RANO-defined tumor progression. In the clinical setting of a tertiary referral hospital, however, many patients are admitted with external MR images. Obtaining pre-surgery qT1 maps would mean an additional MR session, which is time-consuming and may cause discomfort for the patients. Therefore, this pilot study is primarily intended to focus on the feasibility and diagnostic value of qT1 mapping in patients with pathohistologically proven glioblastoma. Nonetheless, the results are promising and encourage to conduct future studies evaluating this method, particularly in therapy-naïve glioblastoma patients.
Overall, this pilot study uncovers a putative role for qT1 mapping in detecting tumor tissue without using GBCA, a method that could have major implications for daily clinical practice and would help avoid subjecting patients to adverse events evoked by GBCA administration. This study encourages validation in a larger trial.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
This study is a part of a prospective, non-interventional pilot MRI study of adult patients with histopathologically confirmed primary glioblastoma or gliosarcoma. All patients signed an institutional review board-approved informed consent form prior to enrolment. We monitored these glioblastoma patients with MRI at 6-week intervals after tumor surgery and during standard therapy (according to the Stupp protocol, [3]). From the whole cohort, we selected those GBM patients with at least five monitoring MRIs and progressive disease according to the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Criteria (RANO, [2]) to ensure that only patients with true progression and not pseudoprogression were analyzed.
MRI study protocol
MRI studies were performed at a 3.0 Tesla whole body system MRI (Achieva, Philips Healthcare, The Netherlands) with an 8-channel phased array head coil. Standard MRI included Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery pulse sequences (FLAIR) and T1-weighted (T1w) spin echo sequences pre- and post-injection of GBCA.
The qT1 data were derived by means of an isotropic 3D ultrafast gradient echo (TFE; 1×1×1 mm3 resolution, field of view of 240 × 220 mm2, 120 slices) using radial turbo direction with a profile order of low-to-high for more efficient readout speed and an adiabatic inversion preparation (hyperbolic secant pulse) with five consecutively varying inversion delays (150, 350, 750, 1200, 2300 ms) and parallel imaging. The shot interval (SI) was fixed to 3000 ms with an efficient TFE shot-length of 660 ms (TFE-factor = 105) for the five various inversion delays. Accuracy in the desired clinical T1-range was verified with a phantom containing 12 flasks of distilled water doped with NiCl2.
T1-relaxation times (qT1) were calculated before and following administration of a GBCA (Gd-DO3A-butrol of 0.1 mmol/kg body weight).
Data analysis
In a first step, we generated qT1 maps and subtracted qT1 maps pre-injection of GBCA (pre-GBCA qT1) from respective post-GBCA maps. On these subtraction maps (ΔqT1maps), the contrast- enhancing part of the tumor became visible as a result of T1 shortening. On the ΔqT1 maps, we observed a pronounced, solid contrast-enhancing region corresponding to the enhancement visible on T1w images and a surrounding subtle, cloudy enhancement not visible on conventional T1w images, the latter of which might represent diffuse angiogenic tumor invasion [27]. To differentiate this subtle enhancement from “solid” contrast-enhancing tumor, we introduced a threshold of >50% T1-shortening post-GBCA, which matched well the contrast-enhancing tumor on conventional post-GBCA T1w images.
In a second step, we searched for a reliable pre-GBCA qT1value that may discriminate the solid contrast-enhancing tumor from its surroundings. We used this value as a lower threshold for a color scale, with which we visualized the tumor. We then compared the threshold-based tumor area on pre-GBCA qT1 maps against the “gold standard” contrast-enhancing tumor on ΔqT1 maps.
qT1 maps
We calculated T1-relaxation time maps from the IR-magnitude data with a fixed likelihood estimate for the goodness of the inversion pulse (F=2.0), also accounting for incomplete longitudinal relaxation at the next excitation. Maps were generated by an in-house script in Matlab (release 2014a, MathWorks Inc). We then scaled these maps to obtain similar T1 values in the normal appearing white matter both before and after contrast agent application, which improved the visibility of regions with decreased T1 values after injection of GBCA. Finally, qT1 maps from all time-points of a given patient were then linearly coregistered with reg_aladin (Translational Imaging Grup, http://cmictig.cs.ucl.ac.uk/wiki/index.php/Reg_aladin) to the very first pre-GBCA qT1 map of that patient.
qT1 subtraction maps for contrast-enhancing tumor
Out of the coregistered qT1 maps pre-injection and post-injection of GBCA, we generated subtraction ΔqT1 maps as follows:
On ΔqT1 maps, we defined the contrast-enhancing tumor as regions with >50% T1 shortening after GBCA. To this end, we used the “thresholding” drawing mode of the ITK-SNAP software, which expands manually set seed regions based on an active contour algorithm [28]. For each subject, we placed a small seed within the visible contrast-enhancement and allowed the algorithm to expand this initial contour to the surrounding regions (with >50% T1 shortening) until the final contour encompassed all the visible contrast-enhancement. In cases where the automatically defined contour extended to and beyond the vessels around the tumor, we manually excluded those vessels from the final region of interest.
Overlap between tumor on pre-GBCA qT1 maps and contrast-enhancing tumor
To detect the tumor on pre-GBCA qT1, we encoded any prolongation of qT1 above the predefined cut-off value as a color scale from red to yellow in the ITK-Snap program (http://www.itksnap.org). This assignment allowed rapid visualization of regions with significantly prolonged qT1 and comparing it against the contrast-enhancing tumor on ΔqT1 maps.
Drawing and active contour segmentation tools in ITK-Snap make it possible to easily delineate the area of contrast-enhancing tumor on ΔqT1 maps (gold standard). Using the program's crosshair tool in the drawing mode, the area of contrast-enhancing tumor was compared to the area of qT1 prolongation above the cut-off value on pre-GBCA maps. Then, the percentage overlap – in steps of 10% - was documented and the extent of overlap was categorized into
excellent overlap: defined as ≥ 90% overlap
moderate overlap: defined as 50-89% overlap
poor overlap: defined as 0-49% overlap
To ensure that only true tumor cases were included and to avoid the inclusion of cases of pseudoprogression, we restricted the analysis of time-points to those where at least two previous time-points showed no pseudoprogression.
We further analyzed the residual pre-GBCA qT1 prolongation that did not overlap with the contrast-enhancing tumor. This was done to evaluate whether the non-overlapping areas convert to a contrast-enhancing tumor in a later follow-up MRI. To this end, pre-GBCA qT1 and ΔqT1 maps were compared with those at later time-points.
Statistics
In each patient and at each time-point, we calculated the pre-GBCA qT1 values within the contrast-enhancing tumor and within its surroundings. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis served to determine the optimal cut-off value of pre-GBCA qT1 that discriminates best between pre-GBCA qT1 values of the contrast-enhancing tumor and pre-GBCA qT1 values of its surrounding tissue.
Acknowledgments
None.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There is no conflicts of interest to declare.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
none
REFERENCES
- 1.Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Jr, Cairncross JG. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:1277–1280. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.7.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, et al. Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1963–1972. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.3541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kanal E. Gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCA): Safety overview after 3 decades of clinical experience. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;34:1341–1345. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2016.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McDonald RJ, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, Jentoft ME, Murray DL, Thielen KR, Williamson EE, Eckel LJ. Intracranial gadolinium deposition after contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2015;275:772–782. doi: 10.1148/radiol.15150025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ramalho J, Semelka RC, Ramalho M, Nunes RH, AlObaidy M, Castillo M. Gadolinium-based contrast agent accumulation and toxicity: an update. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:1192–1198. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hatje V, Bruland KW, Flegal AR. Increases in anthropogenic gadolinium anomalies and rare earth element concentrations in San Francisco bay over a 20 year record. Environ Sci Technol. 2016;50:4159–4168. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mottershead JP, Schmierer K, Clemence M, Thornton JS, Scaravilli F, Barker GJ, Tofts PS, Newcombe J, Cuzner ML, Ordidge RJ, McDonald WI, Miller DH. High field MRI correlates of myelin content and axonal density in multiple sclerosis--a post-mortem study of the spinal cord. J Neurol. 2003;250:1293–1301. doi: 10.1007/s00415-003-0192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seewann A, Vrenken H, van der Valk P, Blezer EL, Knol DL, Castelijns JA, Polman CH, Pouwels PJ, Barkhof F, Geurts JJ. Diffusely abnormal white matter in chronic multiple sclerosis: imaging and histopathologic analysis. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:601–609. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jurcoane A, Wagner M, Schmidt C, Mayer C, Gracien RM, Hirschmann M, Deichmann R, Volz S, Ziemann U, Hattingen E. Within-lesion differences in quantitative MRI parameters predict contrast enhancement in multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38:1454–1461. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reichenbach JR, Hacklander T, Harth T, Hofer M, Rassek M, Modder U. 1H T1 and T2 measurements of the MR imaging contrast agents Gd-DTPA and Gd-DTPA BMA at 1.5T. Eur Radiol. 1997;7:264–274. doi: 10.1007/s003300050149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.MacDonald HL, Bell BA, Smith MA, Kean DM, Tocher JL, Douglas RH, Miller JD, Best JJ. Correlation of human NMR T1 values measured in vivo and brain water content. Br J Radiol. 1986;59:355–357. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-700-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bastin ME, Sinha S, Whittle IR, Wardlaw JM. Measurements of water diffusion and T1 values in peritumoural oedematous brain. Neuroreport. 2002;13:1335–1340. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200207190-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Witwer BP, Moftakhar R, Hasan KM, Deshmukh P, Haughton V, Field A, Arfanakis K, Noyes J, Moritz CH, Meyerand ME, Rowley HA, Alexander AL, Badie B. Diffusion-tensor imaging of white matter tracts in patients with cerebral neoplasm. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:568–575. doi: 10.3171/jns.2002.97.3.0568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fu Y, Tanaka K, Nishimura S. Evaluation of brain edema using magnetic resonance proton relaxation times. Adv Neurol. 1990;52:165–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kamman RL, Go KG, Berendsen HJ. Proton-nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation times in brain edema. Adv Neurol. 1990;52:401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971;171:1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chatel M, Darcel F, de Certaines J, Benoist L, Bernard AM. T1 and T2 proton nuclear magnetic resonance (N.M.R.) relaxation times in vitro and human intracranial tumours. Results from 98 patients. J Neurooncol. 1986;3:315–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00165579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reulen HJ, Graham R, Spatz M, Klatzo I. Role of pressure gradients and bulk flow in dynamics of vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg. 1977;46:24–35. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.46.1.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Le Bas JF, Leviel JL, Decorps M, Benabid AL. NMR relaxation times from serial stereotactic biopsies in human brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984;8:1048–1057. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198412000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Araki T, Inouye T, Suzuki H, Machida T, Iio M. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain tumors: measurement of T1. Work in progress. Radiology. 1984;150:95–98. doi: 10.1148/radiology.150.1.6689793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Englund E, Brun A, Larsson EM, Gyorffy-Wagner Z, Persson B. Tumours of the central nervous system. Proton magnetic resonance relaxation times T1 and T2 and histopathologic correlates. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1986;27:653–659. doi: 10.1177/028418518602700606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Curnes JT, Burger PC, Djang WT, Boyko OB. MR imaging of compact white matter pathways. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988;9:1061–1068. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ngo FQ, Bay JW, Kurland RJ, Weinstein MA, Hahn JF, Glassner BJ, Woolley CA, Dudley AW, Jr, Ferrario CM, Meaney TF. Magnetic resonance of brain tumors: considerations of imaging contrast on the basis of relaxation measurements. Magn Reson Imaging. 1985;3:145–155. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(85)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Komiyama M, Yagura H, Baba M, Yasui T, Hakuba A, Nishimura S, Inoue Y. MR imaging: possibility of tissue characterization of brain tumors using T1 and T2 values. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1987;8:65–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Amharref N, Beljebbar A, Dukic S, Venteo L, Schneider L, Pluot M, Manfait M. Discriminating healthy from tumor and necrosis tissue in rat brain tissue samples by Raman spectral imaging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768:2605–2615. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.06.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muller A, Jurcoane A, Kebir S, Ditter P, Schrader F, Herrlinger U, Tzaridis T, Madler B, Schild HH, Glas M, Hattingen E. Quantitative T1-mapping detects cloudy-enhancing tumor compartments predicting outcome of patients with glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 2017;6:89–99. doi: 10.1002/cam4.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage. 2006;31:1116–1128. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]