Figure 2. Silencing lncRNA H19 expression diminishes BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs in vitro.
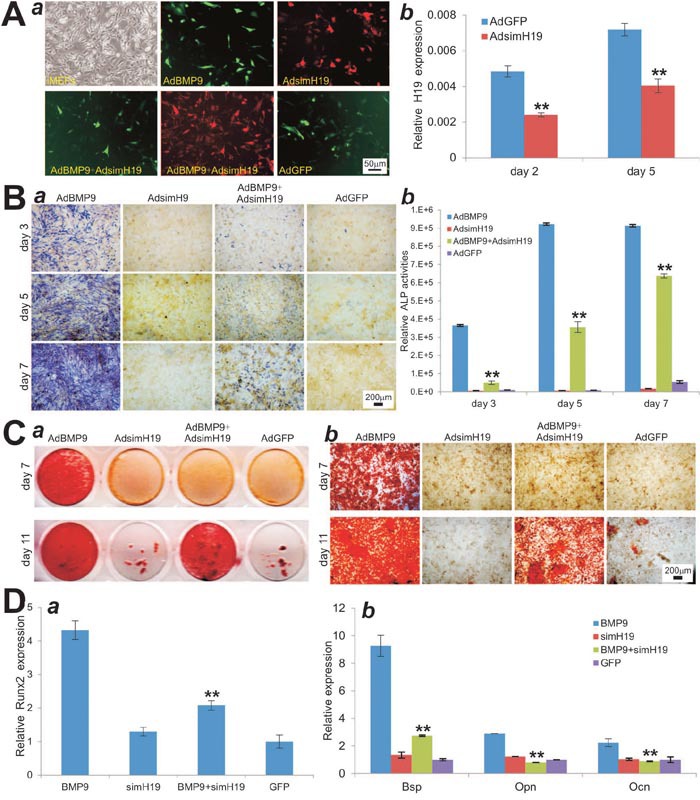
(A) Effective knockdown of mouse H19 expression. (a) The AdsimH19 expressing siRNA targeting mouse H19 transduces iMEF cells with high efficiency in single or combination infection. (b) AdsimH19 silences the expression of H19 at day 2 and day 5. All samples were normalized with the reference gene Gapdh. Each assay condition was done in triplicate. “**” p < 0.001, AdsimH19 vs. AdGFP groups. (B) AdsimH19 inhibits BMP9-induced ALP activity in MSCs. Subconfluent iMEFs were infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP and/or AdsimH19. At the indicated time points, the infected cells were subjected to ALP activity assays by either histochemical staining (a) or quantitative bioluminescence assay (b). Each assay conditions were done in triplicate. Representative staining is shown. “**” p < 0.001, AdBMP9 group vs. AdBMP9+AdsimH19 group. (C) AdsimH19 inhibits BMP9-induced calcium deposit. Subconfluent iMEFs were infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP and/or AdsimH19, and cultured in mineralization medium. At the indicated time points, the infected cells were fixed and subjected to Alizarin Red S staining. Each assay condition was done in triplicate. Representative gross images (a) and microscopic images (20x) (b) are shown. (D) AdsimH19 inhibits BMP9-induced osteogenic regulator Runx2 at day 3 (a) and late osteogenic differentiation marker Bsp, Opn and Ocn at day 5 (b). “**” p < 0.001, AdBMP9 group vs. AdBMP9+AdsimH19 group.
