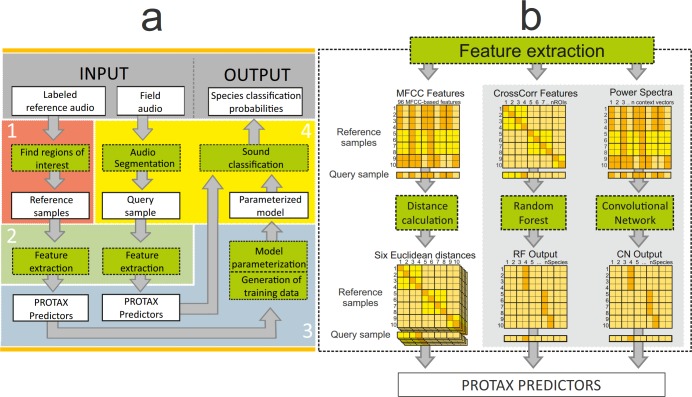
Fig 1. A schematic overview of PROTAX-Sound, a probabilistic classification system for animal sounds.
Input files consist of labeled reference audio and field audio to be classified. The final outputs are the predicted classification probabilities for segments of field audio. Green boxes represent PROTAX-Sound functions; white boxes are inputs and outputs of these functions. The acoustic features and PROTAX-Sound predictors are calculated in the same way for both reference and query samples. The distances calculated from the MFCC features are used as PROTAX-Sound predictors. The cross-correlation features are used as input in the random forest model, the output of which is used to calculate PROTAX-Sound predictors. Mel-scaled log-power spectra of selected frames are used as input in the convolutional neural network, the output of which is used to calculate PROTAX-Sound predictors in the same way as for random forest. Panel a) shows the overall framework and panel b) the feature extraction pipeline (box 2 in panel a) in more detail, illustrated with MFCC features, cross-correlations features classified by Random Forest and power spectra features classified by convolutional neural network.