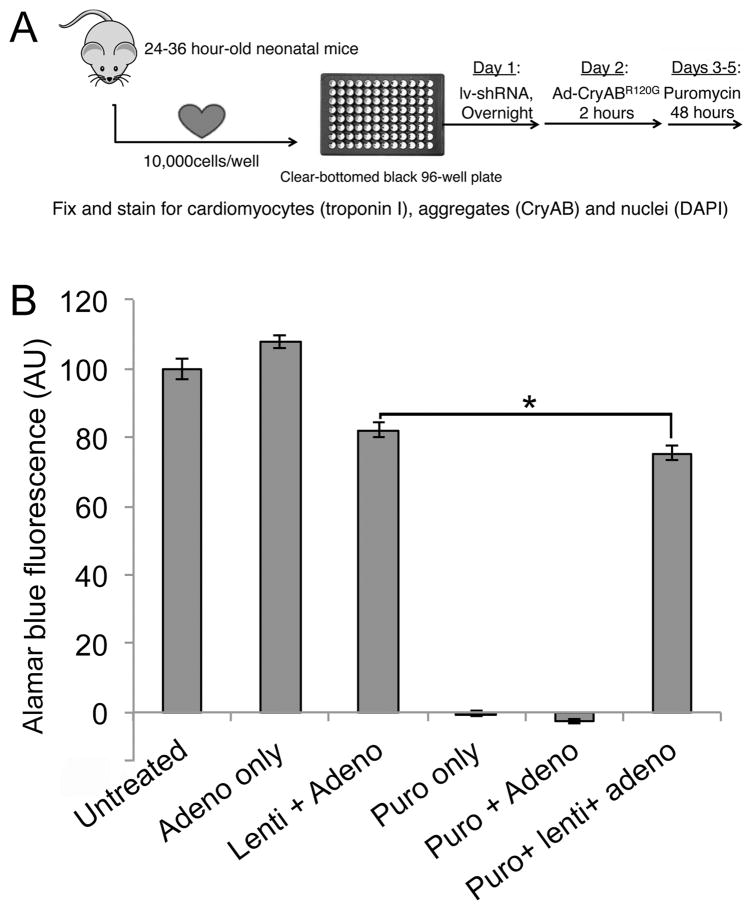
Figure 1. High throughput screen.
A, Screening protocol. Primary cardiomyocytes were harvested from 1–1.5 day old neonatal mice and plated (1×104 cells/well) in 96 well plates. Cells were infected with lentivirus overnight and, after 5 hours of recovery, infected with adenoviruses expressing the aggregate reporter (CryABR120G-tGFP) for 2 hours. After 48 hours, puromycin was added to remove uninfected cells and cells were fixed after an additional 48hrs and counterstained for imaging. B, Viability assay in the presence of viral infection and puromycin selection. The neonatal cardiomyocytes were infected with the indicated constructs. Each lentiviral shRNA construct contained a puromycin-resistance gene to gauge infectivity, as cells infected with lentivirus will be resistant to puromycin treatment. Treating uninfected or adenoviral infected cells resulted in 100% cell death, whereas infection with lentivirus largely preserved cell viability. The small (7%) decrease in Alamar Blue Fluorescence as a measure of cell viability (*P< 0.05), represents a small fraction of cells uninfected by lentivirus, which can be eliminated via puromycin selection.