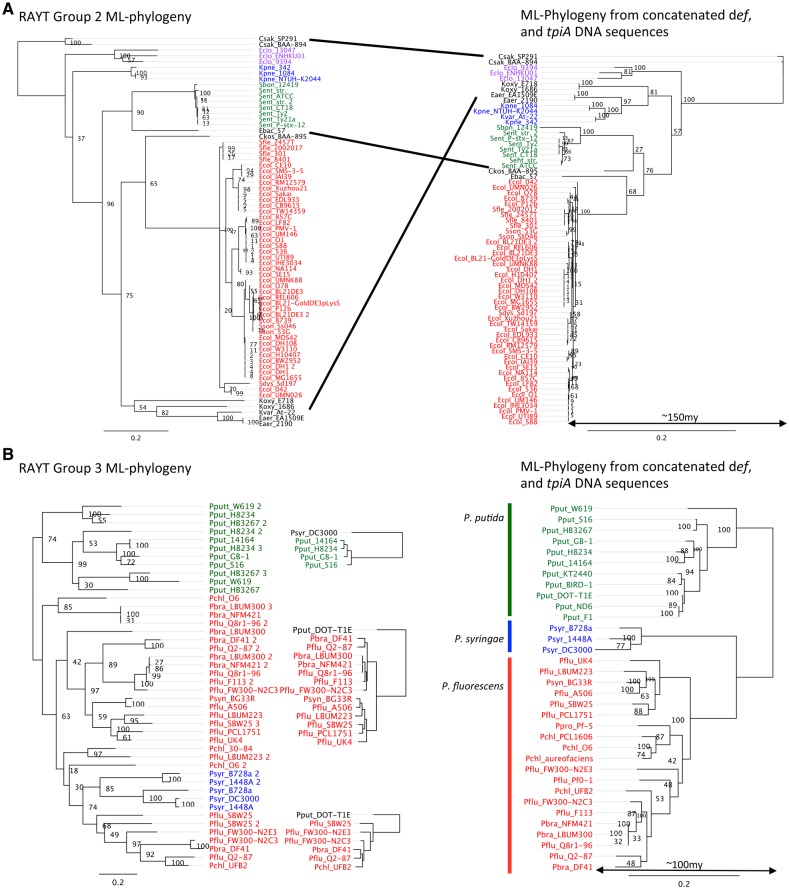
Fig. 6.—
Comparison between RAYT phylogenies and housekeeping gene phylogenies shows vertical RAYT inheritance. (A) Shows the RAYT Group 2 phylogeny and its corresponding housekeeping gene tree of all RAYT Group 2 members that are found in the Enterobacteriaceae. Escherichia, Salmonella, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter cloacae are coloured in red, green, blue, and purple, respectively. The remaining genera are in black and their corresponding positions in the housekeeping gene tree are connected with black lines. The most recent common ancestor is estimated to have lived about 150 Ma from a 16S rDNA tree (Ochman and Wilson 1987). RAYT Group 2 genes occur mostly as single copy genes. (B) Shows the RAYT Group 3 phylogeny and its corresponding housekeeping gene tree for all RAYT Group 3 members that are found in Pseudomonas fluorescens, P. putida and P. syringae. They are coloured in red, green, and blue, respectively. The most recent common ancestor is estimated to have lived about 100 Ma from a 16S rDNA tree (Ochman and Wilson 1987). Small trees in between the housekeeping gene tree and the RAYT tree are corresponding housekeeping trees for the RAYT subtrees. The strain name in black indicates the outgroup. RAYT Group 3 genes occur often in multiple copies per genome. Their evolution is dominated by gene loss and duplication events.