Figure 5. Sensitization to ATR inhibition by A3A is dependent on the ATR checkpoint function.
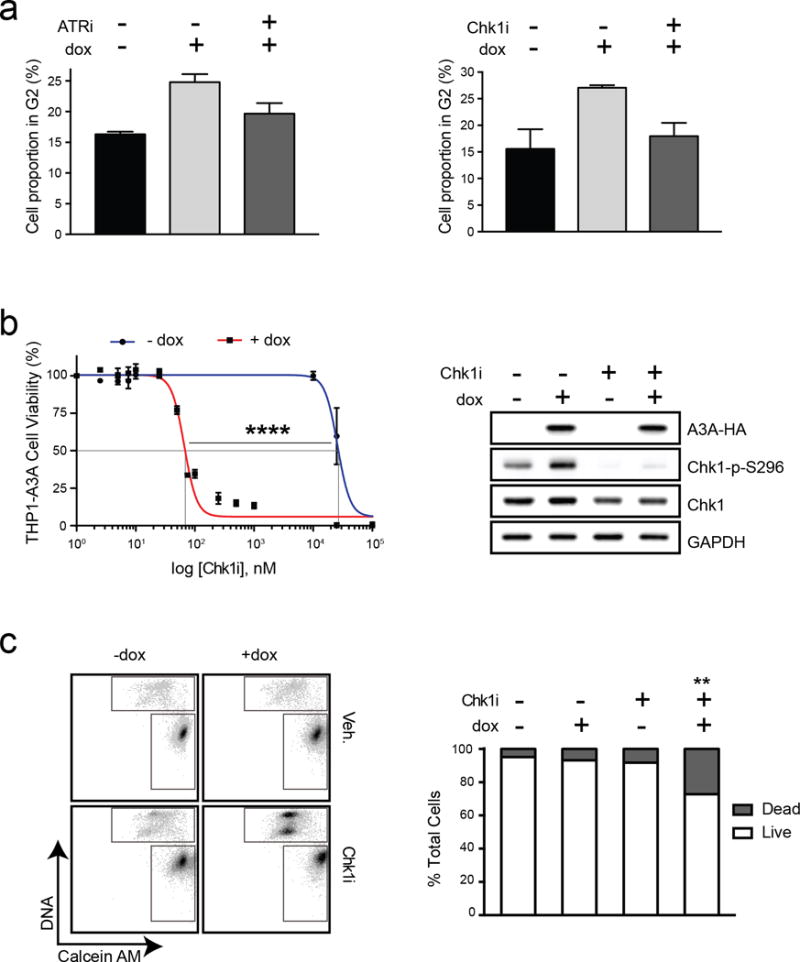
THP1-A3A cells were treated with 1 μg/mL dox to induce A3A expression, and a small molecule inhibitor of ATR or Chk1 kinase prior to analysis. (a) Checkpoint arrest is abrogated by small molecule inhibition of ATR or Chk1. THP1-A3A cells were treated with dox for 48 hours and analyzed for cell cycle progression by propidium iodide staining. Accompanying chart shows fraction of cells in G2 phase before dox induction, after dox induction, and after dox induction combined with kinase inhibitor (80 nM ATRi or 30 nM Chk1i) treatment. Statistical analysis was performed using a paired two-tailed t-test. Error bars indicate SEM. (b) Viability of THP1-A3A cells was measured after treatment with indicated doses of Chk1i. Cell viability was determined by metabolism of a water-soluble tetrazolium salt. Statistical analysis of EC50 was performed using a sum-of-squares F-test. Error bars are SEM. Immunoblotting shows inhibition of Chk1 kinase activity upon treatment with Chk1i (30 nM) indicated by decreased phosphorylation of Chk1 at serine 296. Antibodies to HA, Chk1, and phosphorylated Chk1 (S296) were used. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (c) Cell death was measured by staining THP1-A3A cells with fluorescent-labeled calcein AM (live) and DNA (dead) stains after treatment with dox (1 μg/mL), Chk1i (100 nM), or combinations. The upper gate on the FACS plot includes dead cells and the lower gate includes live cells. Accompanying bar chart shows quantitation of FACS results averaged over three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using a paired two-tailed t-test. Error bars indicate SEM.
