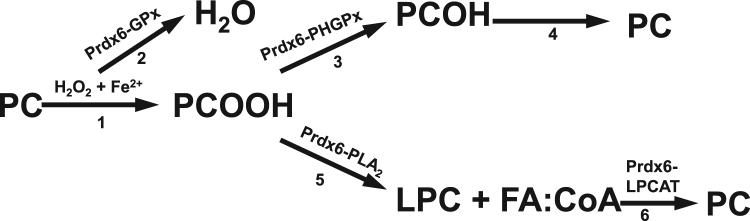
Fig. 4.
Schematic showing the role of Prdx6 in the pathways for oxidation and reduction of cell membrane phospholipids.The reactions are: 1) oxidation of the unsaturated fatty acid (FA) in phosphatidylcholine (PC) by Fe2+ catalyzed generation of ROS; 2) reduction (scavenging) of H2O2 by GSH-dependent GPx activity; 3) reduction by oxidized phospholipid by phospholipid hydroperoxide GPx (PHGPx) activity; 4) reduction of phospholipid alcohols by unspecified reductases; 5) hydrolysis of oxidized sn-2 FA (FAOOH) in PCOOH by PLA2 to generate lysoPC (LPC) plus an oxidized free FA (not shown); 6) reacylation of LPC with free FA:CoA by LPC acyl transferase (LPCAT) activity (the importance of the Prdx6-LPCAT activity in cell membrane repair has not yet been demonstrated experimentally). The net result is the regeneration of reduced phospholipid following an oxidative event.