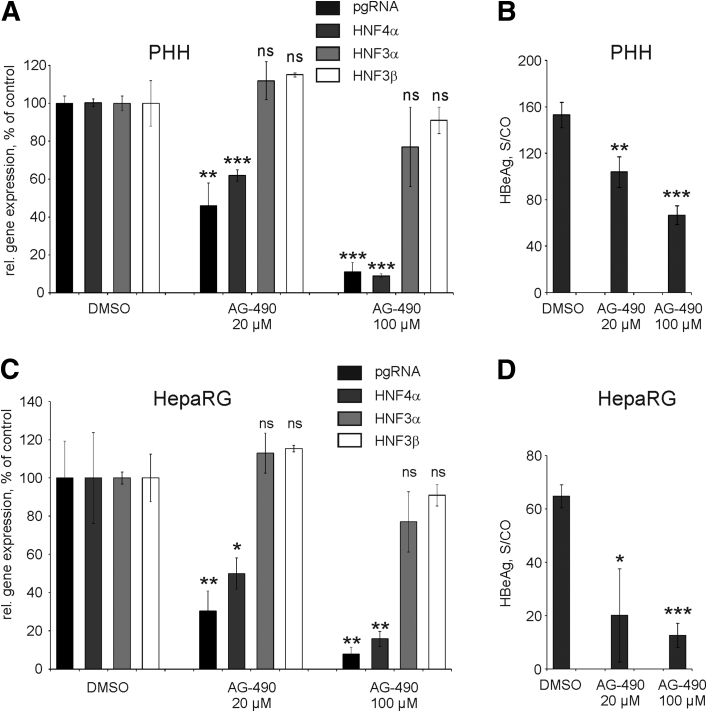
Figure 8.
Inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 by AG-490 and its consequences for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. HBV-infected PHHs (A, B) or HepaRG cells (C, D) were treated for 24 hours either with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or with AG-490 (20 or 100 μM). (A, C) Expression levels of HBV pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) and HNF4α, HNF3α, and HNF3β genes were determined by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Gene expression levels in HBV-infected cells treated with DMSO were set to 100%. (B, D) Levels of hepatitis B early antigen (HBeAg) secreted into the cell culture medium were determined by as signal-to-control (S/CO) ratio by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay at 24 hours after treatment with AG-490. All values are shown as mean ± SD, statistical significance was calculated relative to the respective DMSO-control sample (n = 3; *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; Student's t test). ns, not significant; PHH, primary human hepatocytes.