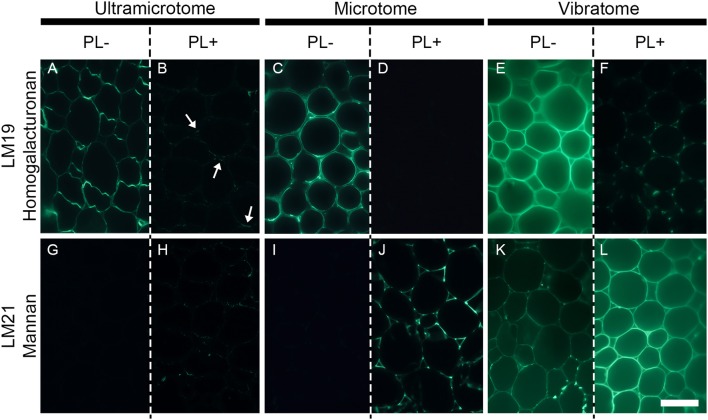
Figure 5.
The efficiency of enzymatic pre-treatment depends of the sample preparation. The figure shows the impact of pectate lyase pretreatment on indirect immunolabeling of the LM19 homogalacturonan and the LM21 mannan epitopes in pith parenchyma cells of transverse A. thaliana stem sections. The presence of the LM19 homogalacturonan epitope is ubiquitous in the walls of pith parenchyma cells and the degradation of homogalacturonan with pectate lyase results in a severe reduction of LM19 detection and an increased detection of the LM21 mannan epitope. The immunolabeling obtained after enzymatic pretreatment showed nuances of enzymatic efficiency between the different methods of sample preparation. (A,B,G,H) Section embedded in resin and cut with an ultramicrotome. (C,D,I,J): Sections embedded in wax and cut with a microtome. (E,F,K,L): Sections coated in agarose and cut with a vibratome. (A–F) Representative sections immunolabeled with the LM19 homogalacturonan antibody. (G–L): Representative sections immunolabeled with the LM21 mannan antibody. (A,C,E,G,I,K) show sections incubated for 2 h with phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) (PL-) prior to immunolabeling. (B,D,F,H,J,L) show sections incubated for 2 h with pectate lyase in a CAPS buffer (pH 10) (PL+) prior to immunolabeling. The parameters used to capture these micrographs were identical between the pre-treatments. However, the time of exposure differed for both antibodies and for each method of sample preparation. The shortest and longest times of exposure were taken for the sections cut with a vibratome and an ultramicrotome, respectively. The arrows in B highlight regions where residual traces of the LM19 epitopes are detected after pectate lyase pre-treatment. Scale bar: 70 μm.