FIGURE 5.
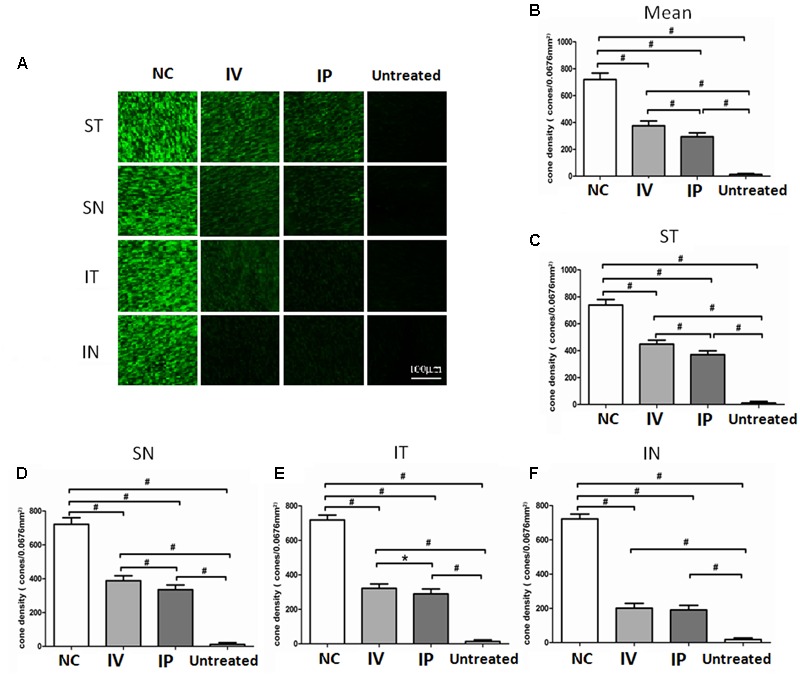
Topographic effects of IV and IP injections on cone photoreceptors. (A) The PNA immunostaining of regional cone photoreceptors in the retinal wholemounts. (B) The cone density of untreated group was significantly smaller than the normal controls (P < 0.01). The cone densities of both IV and IP treated groups were significantly larger than the untreated group (P < 0.01). The mean cone density of the IP treated group was significantly smaller than the IV treated group (P < 0.01; n = 10). (C–F) In both IV and IP treated groups, the cone density of the ST quadrant was significantly larger than the other three quadrants (P < 0.01). The cone density of the IV treated group was significantly larger than the IP treated group respectively in the ST, SN, and IT quadrant. In the IN quadrant, the cone density of the IV treated group was not significantly different from the IP treated group (P > 0.05; n = 10). (All the values were presented as mean ± SD; ∗P < 0.05, #P < 0.01 for differences compared between the animal groups).
