Fig. 4.
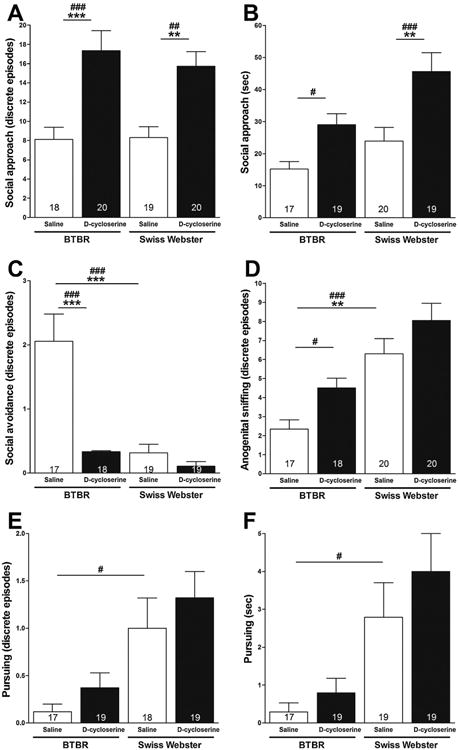
Effect of d-cycloserine on dimensions of sociability in session III. Bars represent means ± SEM of the number of discrete episodes of social approach (A), amount of time spent approaching (B), discrete episodes of social avoidance (C), discrete episodes of anogenital sniffing (D), discrete episodes of pursuit (E), and time spent pursuing (F) made by 4-week-old male BTBR and Swiss-Webster mice toward a 4-week-old male ICR stimulus mouse when test and stimulus mice were allowed to interact freely 20 min after treatment with d-cycloserine (320 mg/kg, ip) or saline. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 significance of post hoc comparisons using Fisher's LSD Multiple Comparison Test.**p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 significance of post hoc comparisons using the Tukey–Kramer Multiple Comparison Test. Numbers in bars represent group sizes.
