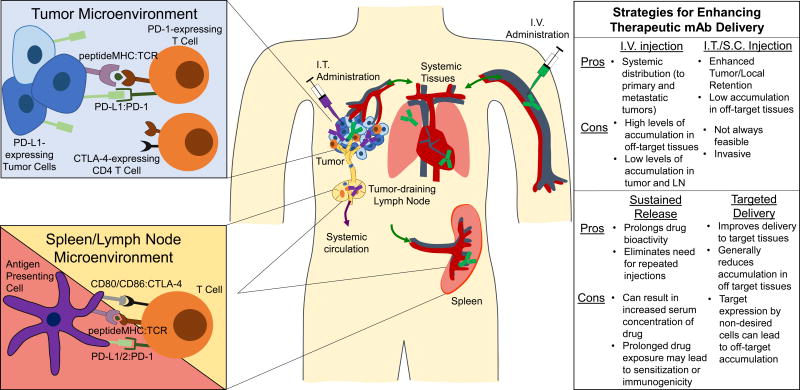
Figure 1.
In the context of cancer, checkpoints are active within tumors and secondary lymphoid tissues. Left, Canonical and non-canonical checkpoint signaling in tumors and secondary lymphoid tissues. Right, Routes of drug administration and drug delivery systems that improve mAb delivery to target tissues with their relative advantages and limitations in conferring enhanced drug bioactivity and potential for toxicity. I.V., intravenous; I.T., intratumoral; S.C., subcutaneous; LN, lymph node. Green and purple syringe, mAb and lines roughly indicate distribution profiles resulting from i.v. and i.t. administration of mAb, respectively.