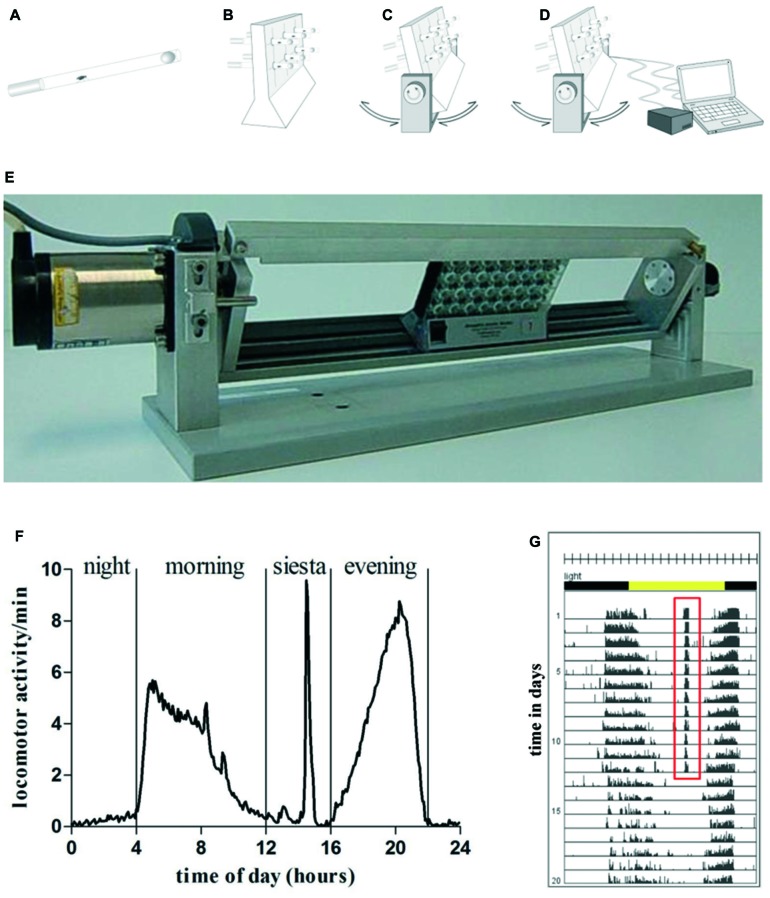
Figure 1.
Graphic depiction of swing boat device (A–D). Flies were inserted into a glass tube, that was closed with food on one side and with foam material on the other side (A). Glass tubes were put into Drosophila activity monitoring (DAM) (B) that was fixed on the swing boat device. During daily 30 min training period the tubes alternately turned 30° to each side so that the top and bottom ends of the fly tubes rotated and induced a negative geotaxis response (C). The device was connected to the steering unit which allowed defining speed, turning angle und frequency of turns (D). A single swing boat device that can carry up to three DAMs (E). (F) Daily activity of wild type fly undergoing 30 min of daily activity induction. One full day is divided in four activity episodes: night, morning, siesta and evening. During the time of siesta sleep when exercise units were given the animal shows pronounced locomotor activity. (G) Actogram of exemplary wild type fly undergoing 12 days of activity induction. Training period is represented by days 1–12, the post-training period comprises days 13–20. Total number of movements was summed at the end of each 5-min interval over the entire time of experiment. Each day (rows) was visualized in 288 bars each representing one 5-min interval. A 12:12 h light dark cycle (LD12:12) is shown by environmental bars (lights on 8 am: ZT0, yellow color; lights off: ZT12, gray color). Red (ZT7) marks activity at this time.