Figure 1.
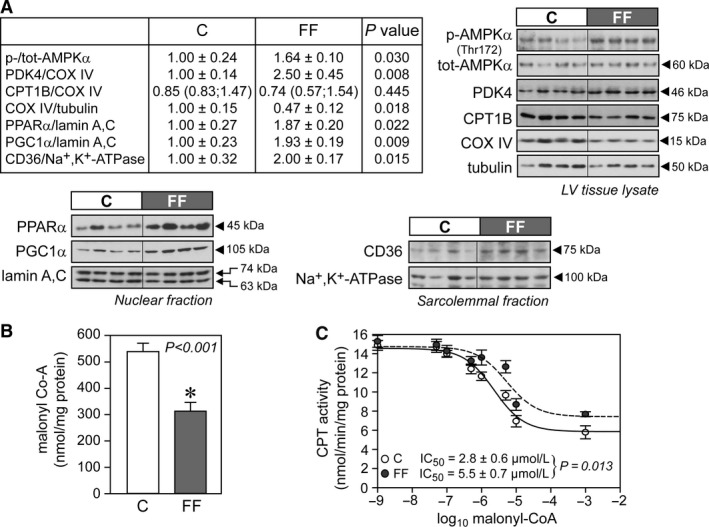
Increased cellular and mitochondrial fatty acid uptake in hearts of fructose‐fed rats. (A) Representative immunoblots and densitometric quantification of cellular AMPK, PDK4, CPT1B, and COX IV, nuclear PPAR α and PGC1α, and plasma membrane CD36 (n = 6–7/group). (B) Malonyl‐CoA content from total cardiac tissue samples (n = 7/group). (C) Semi‐logarithmic plot of CPT activity at graded malonyl‐CoA concentrations (0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, and 1000 μmol L−1; n = 7/group), with averaged IC 50 values calculated from independent plots for each heart in each independent treatment group. Data were normalized to mitochondrial protein concentration. Results are mean ± SE. C, control rats; FF, fructose‐fed rats; AMPK, 5′ AMP‐activated protein kinase; CD36, fatty acid translocase; COX IV, complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase); CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; PDK4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; PPAR α, peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor alpha; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor gamma coactivator 1‐alpha.
