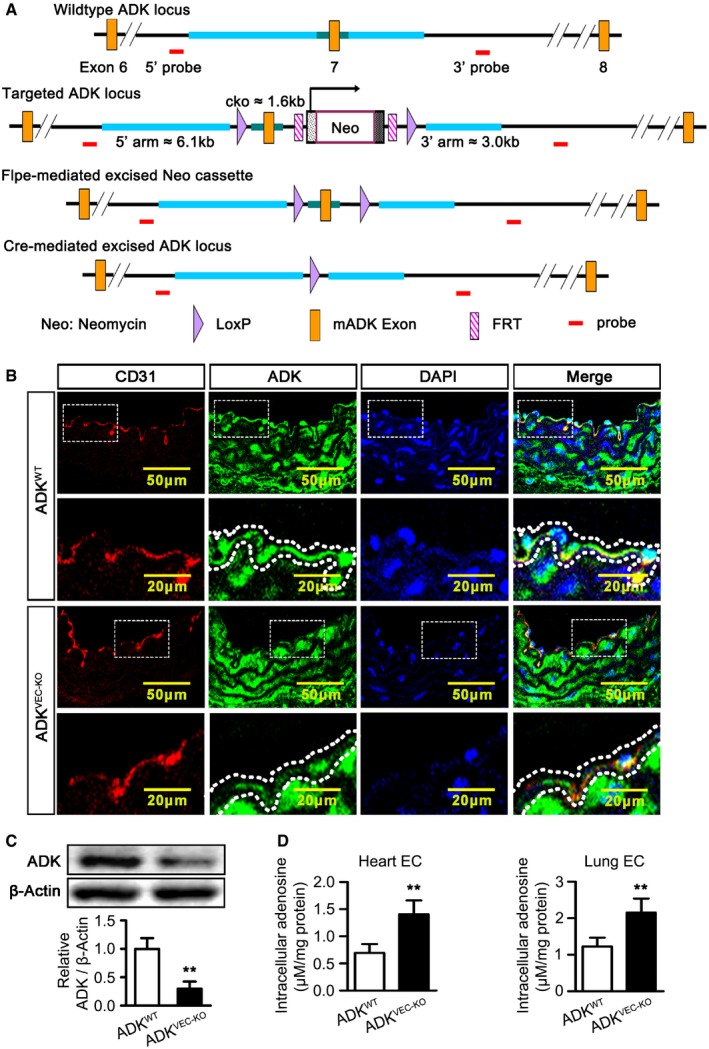
LoxP targeting of ADK. The targeting construct introduces the loxP sites flanking exon 7 of the ADK gene. Floxed mice were then crossed with a mouse in which expression of Cre recombinase is driven by an endothelial‐specific promoter associated with the vascular endothelial cadherin (Cdh5).
Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 and ADK on aortic endothelium of ADKWT, Cdh5‐Cre (ADKVEC‐KO), and ADKWT mice (n = 4 mice per group). Dotted lines outline the arterial endothelium.
Western blot analysis of ADK in MAECs isolated from ADKWT and ADKVEC‐KO mice. Results are from four independent experiments.
Quantification of intracellular adenosine by HPLC in mouse endothelial cells isolated from hearts and lungs. Results are from four independent experiments.
Data information: For all bar graphs, data are the means ± SD, **
P <
0.01 for ADK
VEC‐KO vs. ADK
WT; unpaired, two‐tailed Student's
t‐test. The exact
P‐values are specified in
Appendix Table S1.
Source data are available online for this figure.