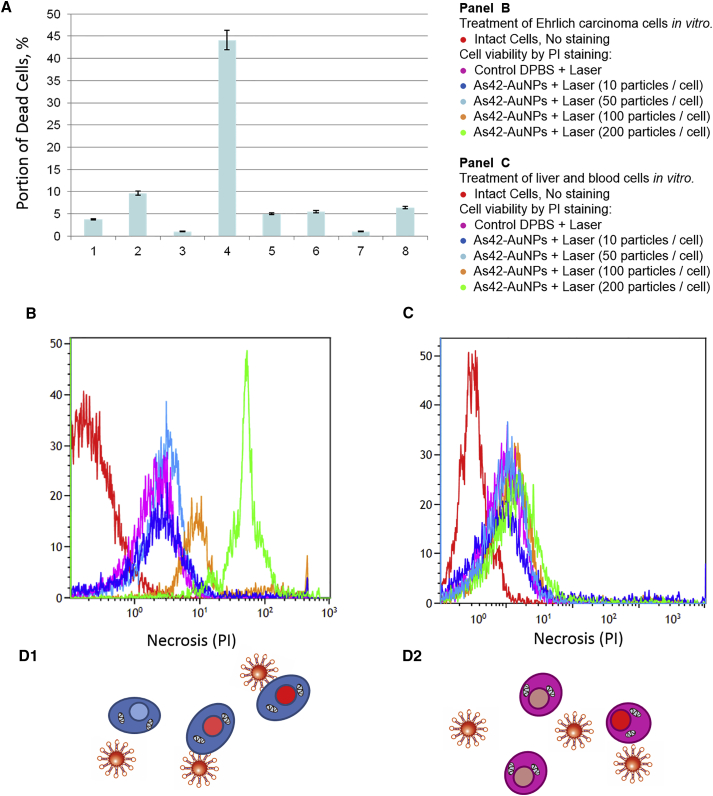
Figure 3.
Effects of Photothermal Therapy of Ehrlich Carcinoma Cells Depending on the Presence of Gold Nanoparticles and/or DNA Aptamers In Vitro
(A) Portions of dead cells were measured using trypan blue 3 hr after treatment in different experimental models. 1, intact Ehrlich carcinoma cells; 2, Ehrlich carcinoma cells after a 4-min laser irradiation; 3, Ehrlich carcinoma cells incubated with As42-AuNPs; 4, Ehrlich carcinoma cells preincubated with As42-AuNPs after 4 min of irradiation; 5, Ehrlich carcinoma cells incubated with free aptamer As42; 6, Ehrlich carcinoma cells incubated with free aptamer As42 after 10 min of irradiation; 7, Ehrlich carcinoma cells incubated with AG-AuNPs; 8, Ehrlich carcinoma cells incubated with AG-AuNPs after 4 min of irradiation. (B) Viability of Ehrlich cells after plasmonic photothermal therapy in vitro with As42-AuNPs (in the ratios of 10, 50, 100, and 200 AuNPs per cell). (C) Viability of liver and blood cell mixture after plasmonic photothermal therapy in vitro with As42-AuNPs (in the ratios of 10, 50, 100, and 200 AuNPs per cell). PI, propidium iodide. (D) Schematic representation of the Ehrlich, liver, and blood cell viability measurements after plasmonic photothermal treatment. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM.