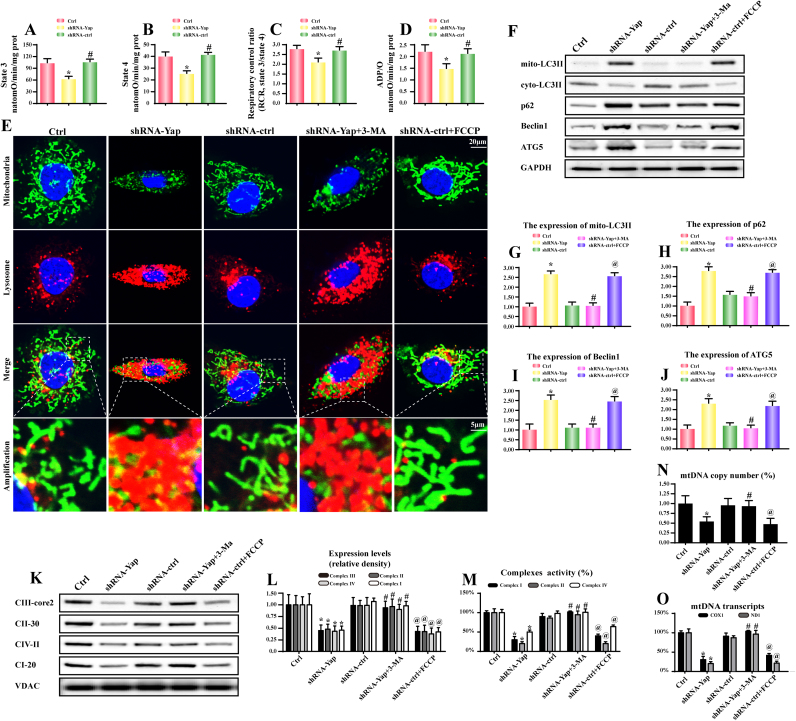
Fig. 4.
Yap-related energy disorder was due to excessive mitophagy. A-D. Effect of Yap deletion on state 3 respiration, state 4 respiration, respiratory control ratio (RCR [state 3/state 4]), and number of nmol ADP phosphorylated to atoms of oxygen consumed (ADP/O). E. The mitophagy activity was examined via the overlap of mitochondria and lysosome. Compared to the control cells, Yap-deleted HepG2 cells had more lysosome containing mitochondria. 3-MA was the inhibitor of mitophagy and 3-MA could alleviate the promotive effect of Yap deficiency on mitophagy. FCCP was the inducer of mitophagy, which was used as the positive control group. F-J. The change of proteins related to mitophagy. K-L. The content of mitochondrial electron respiratory complex (ETC). Yap caused a significant drop in ETC contents. But this tendency was reversed by 3-MA. M. The changes in ETC I, II, and V activities were measured spectrophotometrically. Yap deficiency was associated with the ETC inactivity which was reversed by mitophagy inhibition via 3-MA. N. The mtDNA copy number was assessed by complex IV segment. O. The transcript level of mtDNA was reflected by two different components: NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (ND1) encoded by the light chain of mtDNA and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COX I) encoded by the heavy chain of mtDNA. *P < 0.05 vs. control group; #P < 0.05 vs. shRNA-Yap group, @ P < 0.05 vs. shRNA-ctrl group.