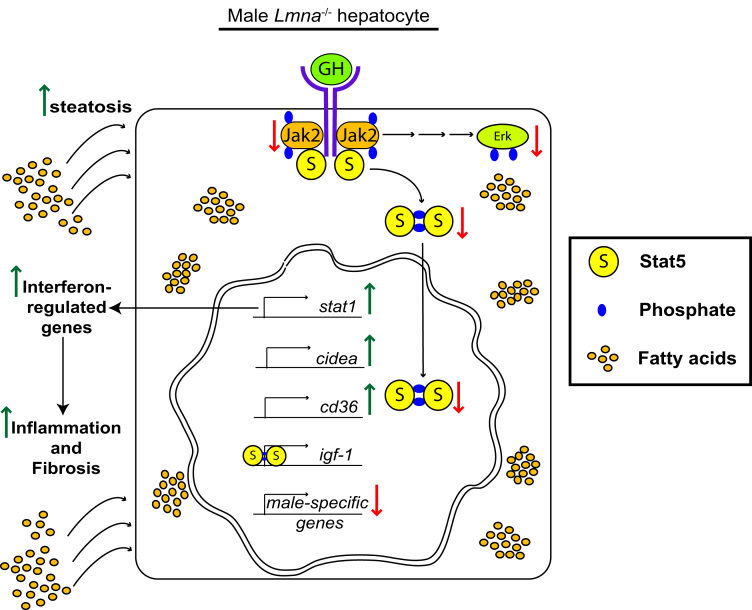
Figure 13.
Absence of lamin A/C in hepatocytes interferes with GH signaling in male hepatocytes. The schematic summarizes our findings. Lmna deficiency is responsible for the following: (1) alters nuclear shape; (2) inhibits growth hormone receptor–mediated Jak2, Stat5, and Erk phosphorylation; (3) decreases the expression of Stat5-dependent male-specific genes; (4) increases expression of the Stat5-regulated fatty acid translocator CD36, (5) up-regulates Cidea transcription, and (6) increases Stat1 messenger RNA and protein expression and activation, resulting in the induction of interferon-regulated genes. These alterations lead to hepatocyte storage of excess fatty acids with consequent induction of hepatic inflammation and fibrosis upon feeding with a HFD.