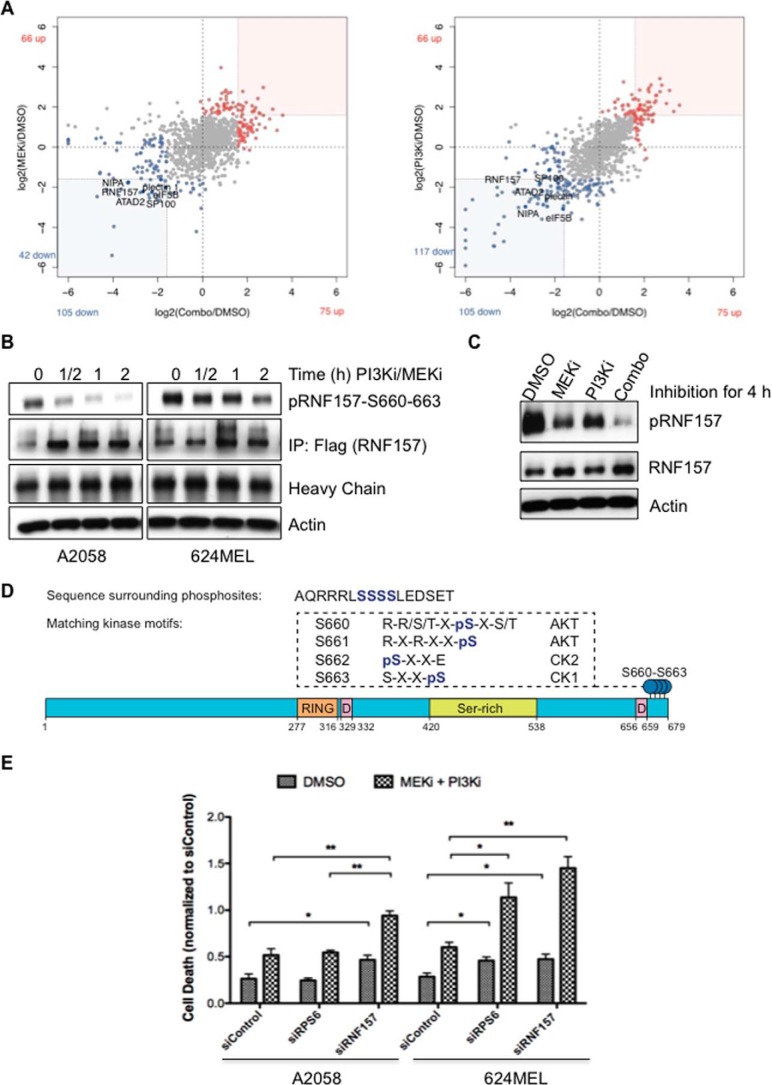
Figure 1.
Phosphoproteomic identification of PI3K/MAPK pathway nodes. A, scatter plots illustrate peptide phosphorylation changes after single inhibition of MAPK or dual inhibition (Combo) of MAPK and PI3K pathways in A2058 cells. B and C, Western blotting confirmed the decreased phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated FLAG-tagged RNF157 (B) and endogenous RNF157 (C) in response to dual (0.25 μm each for the times indicated (B)) and single inhibition (0.5 μm each for 2 h) with the phosphospecific RNF157 antibody. D, schematic diagram of protein domains of RNF157 and some key facts. RING domain contains a Cys3-His-Cys4 motif that binds two zinc cations. Most of the RING domain-containing proteins function as ligases. The D-boxes are consensus sequences for targeted polyubiquitination. The phosphorylation sites identified by MS-based phosphoproteomics are located at the C terminus of RNF157 and represent the phosphorylation motifs for AKTs and casein kinases (CK). E, inhibition of RNF157 enhances cellular efficacy by PI3K inhibitor (PI3Ki) pictilisib (GDC-0941) and MEK inhibitor (MEKi) cobimetinib (GDC-0973). A2058 and 624MEL cells were treated with siRNA against RNF157 or RPS6 or transfected with non-targeting siRNA as a control for 48 h and subsequently treated with GDC-0973 and GDC-0941 (0.03125 μm each (A2058 cells) or 0.0625 μm each (624MEL cells)) for 24 h. Cell death was evaluated by quantifying BrdU incorporation and cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments, respectively. Data from three independent experiments are shown. Error bars represent ±S.D. of the mean. A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. p values are designated with asterisks as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01. IP, immunoprecipitation.