Figure 1.
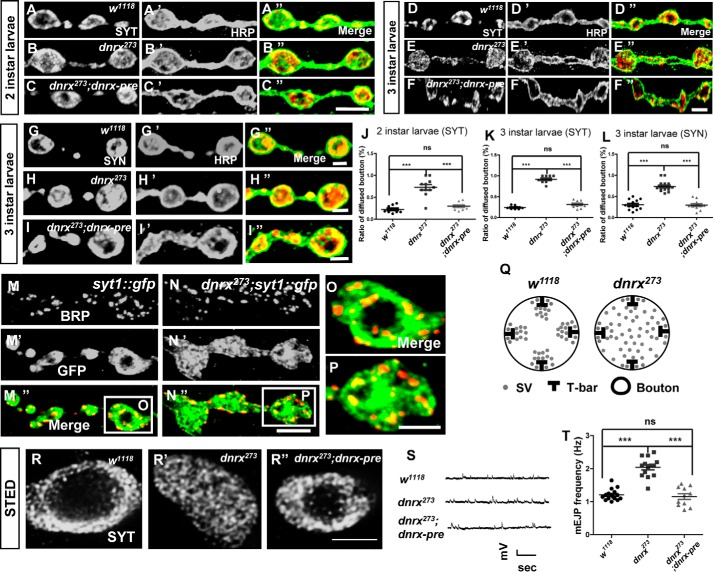
DNRX is necessary for synaptic terminal aggregation and release of SVs. A–C″, synaptic boutons of wild-type (A–A″), dnrx mutant (B–B″), and pre-synaptic rescue (C–C″) at two instar larvae stage double stained for SYT (red) and HRP (green), which labels the pre-synaptic SVs and neuronal membrane, respectively. D–F″, synaptic boutons of wild-type (D–D″), dnrx mutant (E–E″), and pre-synaptic rescue (F–F″) at third instar larvae stage double stained for SYT (red) and HRP (green), which labels the pre-synaptic SVs and neuronal membrane, respectively. G–I″, synaptic boutons of wild-type (G–G″), dnrx mutant (H–H″), and pre-synaptic rescue (I–I″) at third instar larvae stage double stained for SYN (red) and HRP (green), which labels the pre-synaptic SVs and neuronal membrane, respectively. J, quantification of the SYT-diffused boutons ratio at two instar larvae stage in muscle 4 shows that dnrx mutants have disturbed the distribution of SVs and this phenotype can be rescued by pre-synaptic DNRX. K, quantification of the SYT-diffused boutons ratio at the third instar larvae stage in muscle 4 shows that dnrx mutants have disturbed the distribution of SVs and this phenotype can be rescued by pre-synaptic DNRX. L, quantification of the SYN-diffused boutons ratio at third instar larvae stage in muscle 4 shows that dnrx mutants have disturbed the distribution of SVs and this phenotype can be rescued by pre-synaptic DNRX. M–N″, confocal images of third instar larvae NMJ boutons double labeled with anti-BRP (red) and anti-GFP (green) in syt::gfp (M–M″), and dnrx273,syt::gfp mutants (N–N″) showing that loss of DNRX disrupts the distribution of terminal SVs. O–P, amplified confocal images of single third instar larvae NMJ bouton double labeled with anti-Brp (red) and anti-GFP (green) in syt::gfp (O), and dnrx273,syt::gfp (P) showing the dispersed distribution of SVs in dnrx mutants. Q, representative diagrammatic sketch of SVs in single bouton of wild-type and dnrx mutant. R–R″, STED images of third instar larvae single bouton of wild-type (R), dnrx mutant (R′), and pre-synaptic rescue (R″) labeled with SYT, showing the SVs were diffused in dnrx mutant and can be rescued by pre-synaptic DNRX. S, representative traces of spontaneous responses of indicated genotypes. T, quantification of mEJP frequency of the indicated genotypes, showing that the mEJP frequency was increased in dnrx mutant and the DNRX could fully rescue the defects at pre-synapse. Data are mean ± S.E. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; and *, p < 0.05. ns, not significant. Two-tailed Student's t tests were used to compare genotypes. Scale bar, 5 (A–C″), 5 (D–F″), 2 (G–G″), 2 (H–H″), 2 (I–I″), 5 (M–N″), 2.5 (O–P), and 2.5 μm (R–R″).