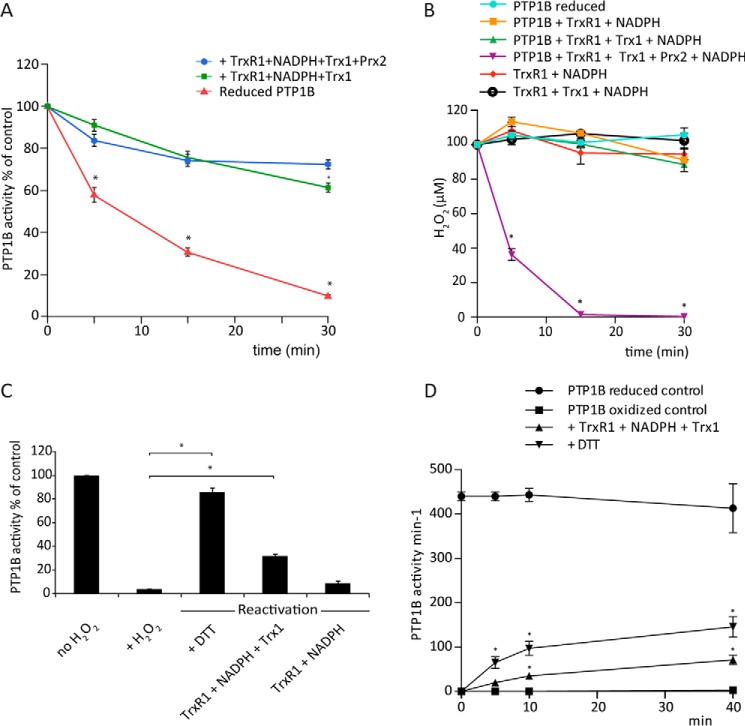
Figure 4.
The Trx system reverses H2O2-inactivated PTP1B. A, reduced PTP1B (600 nm) was preincubated for 30 min either alone or with 2 μm Trx1, 0.5 μm TrxR1 (specific activity, 9.75 units/mg), and 200 μm NADPH, with or without Prx2 (10 μm). H2O2 (100 μm) was then added, and samples were taken at 5, 15, and 30 min for measurement of PTP activity (n = 3; mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05). B, H2O2 consumption by PTP1B and components of the Trx/Prx2 system. Combinations of Trx1 (2 μm), TrxR1 (0.5 μm, 18 units/mg), Prx2 (10 μm), and NADPH (200 μm) with and without reduced PTP1B (600 nm) were treated with 100 μm H2O2 at 22 °C, and concentrations of H2O2 at the indicated time points were determined by ferrous oxidation of xylenol orange assay (n = 3; mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05). C, reactivation of H2O2-inactivated PTP1B (cleaved form). Reduced PTP1B was treated with 1 mm H2O2 for 5 min and then with catalase to remove residual H2O2 and reactivated with 10 mm DTT or TrxR1 (2.5 μm) (specific activity, 18 units/mg) and NADPH (1 mm) with or without Trx1 (10 μm). After 45 min at 22 °C, samples were analyzed for PTP activity (n = 3; mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05). D, reactivation of H2O2-inactivated PTP1B catalytic domain. Reduced PTP1B was treated with 1 mm H2O2 for 5 min and then with catalase and reactivated with 10 mm DTT or TrxR1 (2.5 μm) (specific activity, 22 units/mg), NADPH (300 μm), and Trx1 (10 μm). After 5, 10, and 40 min at 22 °C, samples were analyzed for PTP activity (n = 3; mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05).