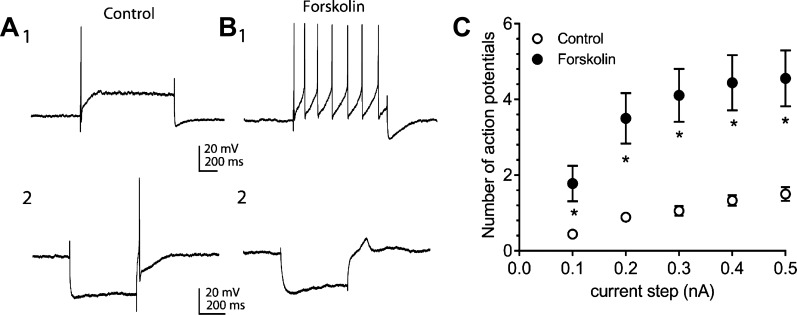
Fig. 1.
Forskolin can increase cardiac neuron excitability and the rectification in hyperpolarizations elicited by constant current injection. A1 and B1: example recording of action potentials elicited by a 1,000 ms, 0.3 nA depolarizing step before (A1) and during 5 µM forskolin exposure (B1). A2 and B2: the slight sag (rectification) in the hyperpolarization induced by the constant current step to ~−90 mV (A2) is due to the activation of the hyperpolarization-activated inward current, Ih. This rectification is more evident during 5 µM forskolin exposure (B2), indicative of an enhanced Ih. In this cell, a rebound depolarization followed the termination of the hyperpolarization, which in A2, but not B2, was sufficient in magnitude to elicit an action potential. The resting membrane potential was initially −60 mV, but over the course of the recording, the cell hyperpolarized by a few millivolts such that the rebound depolarization, although still evident, did not reach the threshold for action potential generation. C: averaged excitability curves for different cells before and during exposure to 5 µM forskolin. ○, Averaged excitability curve for 18 cells before forskolin; ●, averaged excitability curve for these same cells during exposure to 5 µM forskolin; *, number of action potentials elicited were significantly greater in forskolin-treated than in control cells.