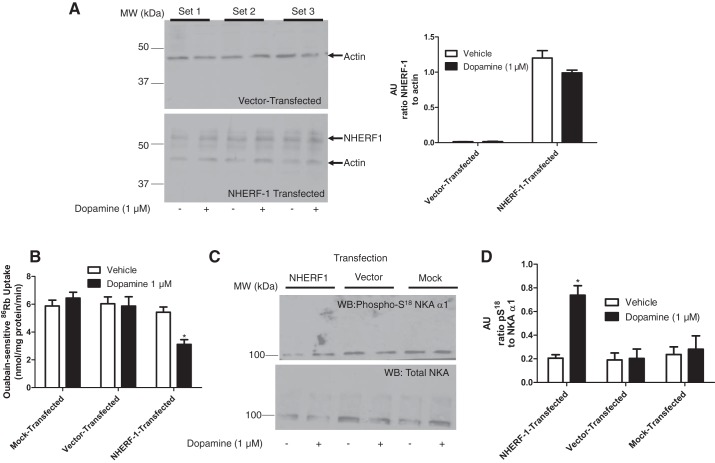
Fig. 4.
Effect of NHERF-1 transfection on dopamine-mediated inhibition of NKA. A: PTCs in primary culture from 22-mo-old F344 rats transiently transfected with Flag-tagged NHERF-1 and cell membrane proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. Top: vehicle- or dopamine-treated cells transfected with empty vector from three individual rats. Bottom: vehicle- or dopamine-treated cells transiently transfected with Flag-tagged NHERF-1 from three individual rats. Bar graph represents data as ratio of band intensity of NHERF-1 to actin (means ± SE) of cultures from 6 individual rats (n = 6 in each group) as arbitrary units (AU). B: PTCs (from A) in primary culture from 22-mo-old F344 rats transiently transfected with vector or Flag-tagged NHERF-1 were treated for 15 min with dopamine (1 μM). Ouabain (4 mM)-sensitive 86Rb uptake was measured. Each bar represents data as nmol 86Rb·mg protein·−1min−1 (means ± SE performed in triplicate (n = 3 rats in each group). *P < 0.05 vs. respective vehicle. C: PTCs in primary culture from 22-mo-old F344 rats transiently transfected with vector or Flag-tagged NHERF-1 were treated for 15 min with dopamine (1 μM). Cell membranes were analyzed by Western blotting using phospho-S18 NKA α1-subunit antibodies (top). Nitrocellulose membranes were stripped and reprobed with NKA antibodies (NKA, α6F, bottom). D: bar graph represents data in C as ratio of band intensity of pS18 to total NKA α1 (means ± SE) (n = 3 rats in each group) as arbitrary units (AU). *P < 0.05 vs. respective vehicle-treated group.