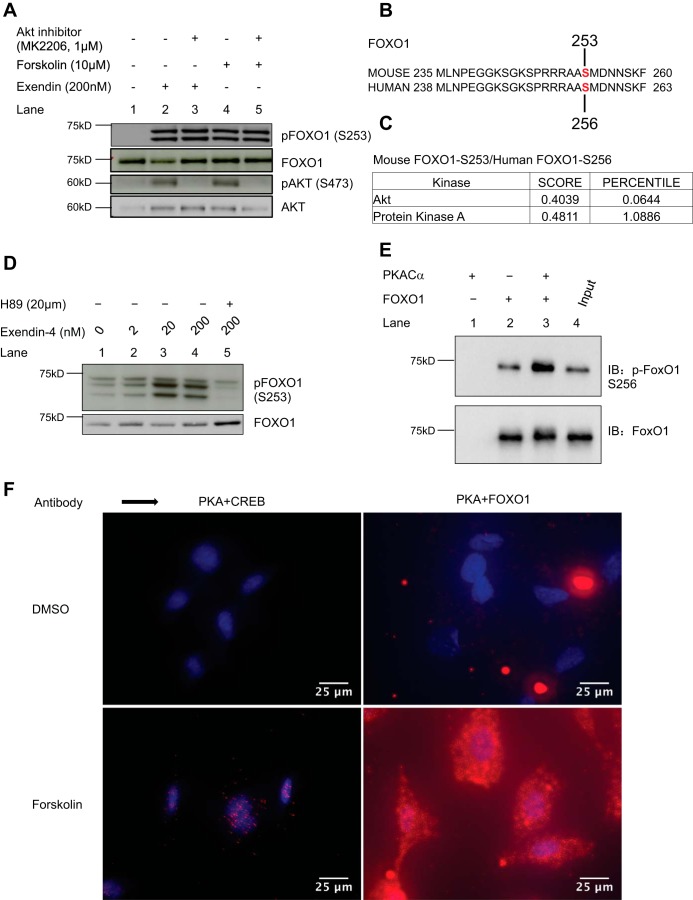
Fig. 3.
GLP1R agonist and forskolin-induced phosphorylation of FOXO1 is PKA-mediated. A: FOXO1 phosphorylation in MIN6 cells induced by either exendin-4 (lane 2, 200 nM) or forskolin (lane 4, 10 μM) is not inhibited by an AKT inhibitor (MK2206, 1 μM, lanes 3 and 5), while phosphorylation of AKT (pAKT-S473) is inhibited as expected (lanes 3 and 5). B: alignment of mouse and human FOXO1 sequences, indicating the S253 and S256 positions, respectively. C: Scansite prediction results showing that both mouse and human FOXO1 can be phosphorylated by PKA at S253 or S256, respectively, with a score of 0.4811 compared with a score of 0.4039 for Akt. D: pretreatment of MIN6 cells with a PKA inhibitor (lane 5, H89, 20 μM) for 30 min inhibits exendin-4 induced phosphorylation of FOXO1 (lanes 1 to 4) (two similar experiments). E: PKA phosphorylates FOXO1 in vitro. Cells (HEK293T cells) transduced with FOXO1 plasmid were collected after 24 h for immunoprecipitation with anti-FOXO1 antibody. The FOXO1 immunoprecipitates were incubated with or without 0.1 μg of purified recombinant active PKA catalytic subunit (PKACα) in kinase buffer (35 mM Tris·HCl pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM CaCl2) containing 100 μM ATP for 30 min at 30°C in a final volume of 40 μl. Reactions were terminated by the addition of concentrated sample buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analysis. Increased S256-FOXO1 phosphorylation was observed upon coincubation with PKACα (top panel, lane 3) compared with vehicle controls (top panel, lane 2). F: proximity ligation assay in MEF cells starved for 24 h in serum-free, low-glucose medium shows increased nuclear colocalization of PKA and CREB upon forskolin (10 μM) stimulation, as expected (compare top left and bottom left panels). Similarly, forskolin treatment increased colocalization of PKA and FOXO1, which was more diffuse and not restricted to the nuclear compartment (two similar experiments).