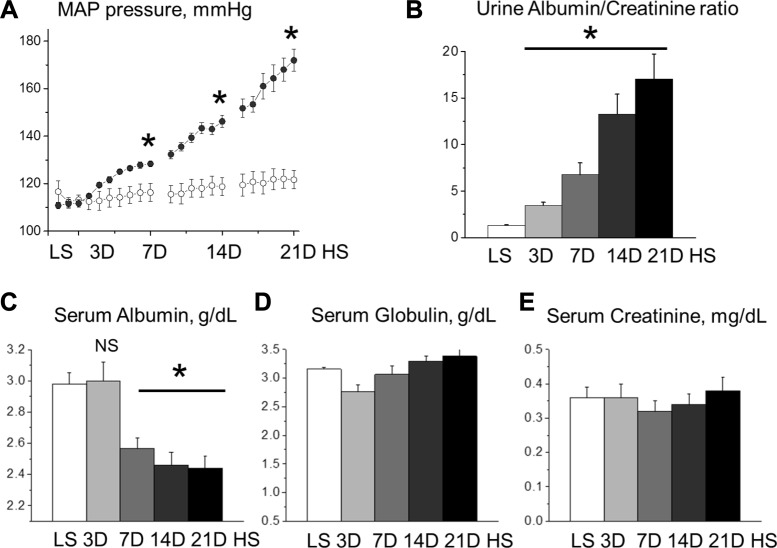
Fig. 1.
Development of salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats. A: mean arterial pressure (MAP) was measured by telemetry in SS rats fed low-salt (LS) followed by high-salt (HS) chow (0.4 vs. 8% NaCl, respectively). B: urine albumin/creatinine ratios demonstrate a rapid development of albuminuria in SS rats fed a HS diet. C: plasma albumin (68 kDa) level in SS rats fed a LS and HS diets, as shown in A. D: concentration of plasma globulins (92–120 kDa) during the development of salt-sensitive hypertension. E: serum creatinine level in SS rats fed LS and HS diet [3 (3D), 7 (7D), 14 (14D), and 21 days (21D)]; n ≥ 7 rats/group for all graphs. *P < 0.05 compared with LS. NS, nonignificant. ○, MAP on the LS diet (NaCl 0.4%); ●, MAPS on HS (NaCl 8%) diets.