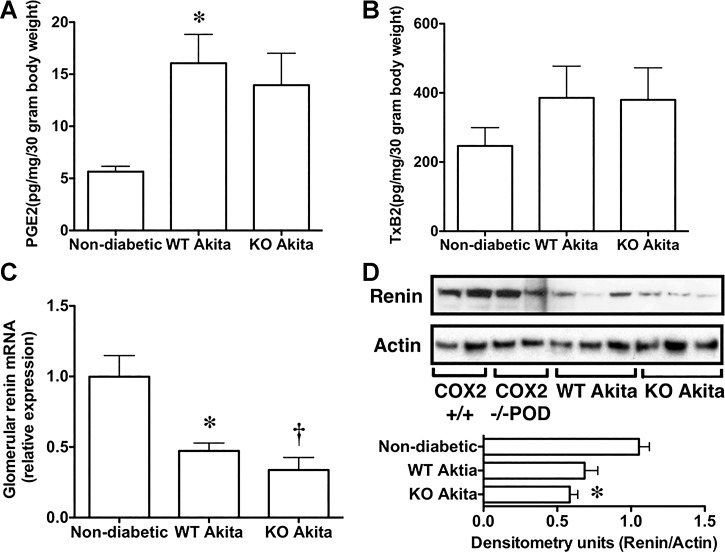
Fig. 6.
Effect of podocyte-specific COX2 KO on urinary eicosanoid excretion and glomerular renin expression. A and B: presence of diabetes significantly enhanced urinary eicosanoid excretion. Both urinary PGE2 metabolites and the urinary thromboxane 2 (TxA2) metabolite TxB2 were increased in both groups of diabetic mice compared to nondiabetic controls. This increase in urinary eicosanoid excretion was statistically significant for PGE2 in WT Akita mice compared to nondiabetic animals. C and D: similarly, the presence of diabetes significantly reduced expression of renin mRNA. Relative expression of renin mRNA was decreased in both groups of diabetic mice compared to nondiabetic controls. For the urinary eicosanoid studies, eight nondiabetic controls, 15 WT Akita, and 11 KO Akita mice were studied. For the renin mRNA studies, eight mice were studied in each group. For the immunoblotting studies, eight nondiabetic, six WT Akita, and six KO Akita mice were studied. For the quantitative RT-PCR studies, eight mice were examined in each group. Statistical analyses were performed using a two-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05 or †P < 0.01 vs. nondiabetic mice.